Differentials
Pseudofolliculitis barbae
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Occurs when hair re-enters the skin adjacent to the exit point from the hair follicle.
Occurs more frequently in men of African descent with black and brown skin (Fitzpatrick skin types 5 and 6).[9][35]
Inflammatory papules develop in the beard area as well as the anterior neck in men who shave regularly.
The mustache area usually does not develop pseudofolliculitis barbae.
Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation often persists following resolution of active lesions. Chronic pseudofolliculitis barbae can lead to the development of firm papules, plaques, hypertrophic scars, and groove formation in the anterior neck and submandibular areas.
INVESTIGATIONS
The advancing end of a curved hair shaft reentering the epidermis results in a histological picture of an invagination of the epidermis.
Accompanied by inflammation, and sometimes microabscess. When the hair enters the dermis, a more exuberant inflammatory response is elicited, and a foreign body giant cell reaction is formed around the tip of the hair.
Acne vulgaris
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Can mimic folliculitis because both diseases affect the pilosebaceous unit.
Although acne vulgaris is typically considered a condition of adolescence and early adulthood, it can persist later into adult life.
Acne primarily affects the face, chest, shoulders and the back. Comedones and inflammatory papules seen in acne are both follicular based.
INVESTIGATIONS
Histopathology shows infundibular dilatation and thinning of the follicular wall with a follicular plug consisting of keratinized cells and sebum. When follicular contents are released into the dermis, there is an inflammatory response mediated by neutrophils and later by histiocytes.
Acne rosacea
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Rosacea is an acneiform condition that occurs more commonly in people 30 years or older.
Typically affects the nose, cheeks, glabella, and chin.
Rosacea can present as diffuse redness with telangiectasia (erythrotelangiectatic subtype), papules and pustules (papulopustular subtype), bulbous swelling of soft tissue (phymatous subtype), or even painful keratitis (ocular rosacea).[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Granulomatous rosaceaFrom the personal collection of Professor Baden, MD [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Granulomatous rosaceaFrom the personal collection of Professor Baden, MD [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Granulomatous rosaceaFrom the personal collection of Professor Baden, MD [Citation ends].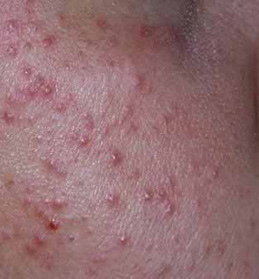
INVESTIGATIONS
Histology of rosacea shows dilatation of vessels in the upper and mid-dermis with a lymphohistiocytic infiltrate around the hair follicles.
Alopecia mucinosa
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Alopecia mucinosa is a condition where follicular mucinosis affecting terminal hair follicles ultimately results in hair loss.
Although follicular papules may be present, some cases present with only well circumscribed patch of alopecia.[36]
INVESTIGATIONS
Histology shows extensive mucin deposition within the outer root sheath and sebaceous gland epithelium, leading to reticular epithelial degeneration.[37]
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer