History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
common
abdominal distension
Symptom of decompensated cirrhosis secondary to ascites in portal hypertension.
jaundice and pruritus
Suggestive of decompensated cirrhosis secondary to reduced hepatic excretion of conjugated bilirubin into the biliary tree. Pruritus is secondary to impaired bile secretion.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Icterus or jaundiceCDC. Dr Thomas F. Sellers/Emory University; used with permission [Citation ends].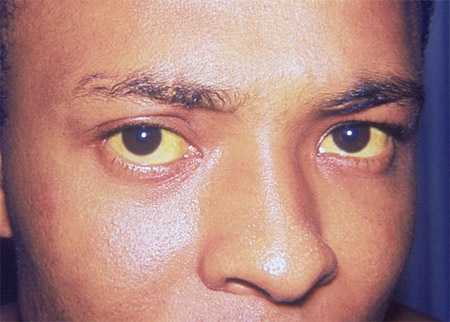
blood in vomit (hematemesis) and black stool (melena)
Symptoms of decompensated cirrhosis secondary to gastrointestinal hemorrhage from gastroesophageal varices in portal hypertension.
hand and nail features (e.g., leukonychia, palmar erythema, spider nevi)
Characteristic physical findings in the hands and nails in chronic liver disease include: leukonychia (white nails) secondary to hypoalbuminemia, polished nails secondary to excessive scratching in pruritus, palmar erythema (redness of thenar and hypothenar eminences), spider nevi (blanch on pressure and spider-like branches fill from a central arteriole), bruising, finger clubbing, and cholesterol deposits in palmar creases in primary biliary cholangitis, and Dupuytren contracture in alcohol-related liver disease.[40][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Preoperative view of a small finger flexion contractureFrom the collection of Dr C.M. Rodner; used with permission [Citation ends].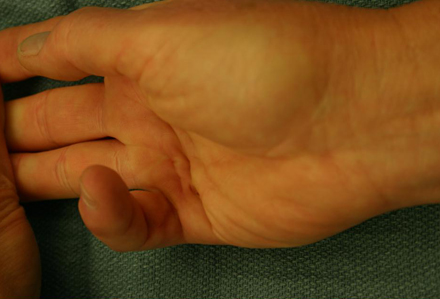
facial features, e.g., telangiectasia, spider nevi, jaundiced sclera
Characteristic physical findings in the face in chronic liver disease include: telangiectasia (red focal lesions resulting from irreversible dilation of small blood vessels in the skin), spider nevi (blanch on pressure and spider-like branches fill from a central arteriole), bruising, rhinophyma, parotid gland swelling, paper-money appearance of the skin (randomly distributed thready blood vessels), and red tongue in alcohol-related liver disease; seborrheic dermatitis, jaundiced sclera, and xanthelasma (yellow plaques on eyelids secondary to lipid deposition) in primary biliary cholangitis.
abdominal features (e.g., collateral circulation, hepatosplenomegaly, distension)
Characteristic physical findings in the abdomen in chronic liver disease include: collateral circulation of the abdominal wall around the umbilicus (caput medusa), bruising, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, abdominal distension (particularly in the flanks) with shifting dullness and fluid thrill secondary to ascites, hepatic bruit (may be present with a vascular hepatoma), and loss of secondary sexual hair and testicular atrophy in men.
uncommon
altered mental status
Symptom of decompensated cirrhosis secondary to portosystemic encephalitis.
Other diagnostic factors
common
constitutional symptoms
Patients with cirrhosis may be asymptomatic or have nonspecific constitutional symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, and weight loss.
lower extremity swelling
Symptom of decompensated cirrhosis secondary to peripheral edema due to hypoalbuminemia.
hepatic fetor
Sweet, putrid smell of the breath in decompensated cirrhosis secondary to portosystemic shunting.
muscle wasting
Common physical finding in chronic liver disease secondary to malnutrition and a hypercatabolic state.
peripheral edema
Sign of decompensated cirrhosis secondary to salt retention and reduced hepatic synthetic function leading to hypoalbuminemia.
uncommon
recurrent infections
Can be present in patients with decompensated cirrhosis secondary to impaired cellular immunity.
decreased libido
Symptom of decompensated cirrhosis secondary to hormonal changes and testicular atrophy, most commonly seen in patients with alcohol-related liver disease and hemochromatosis.
chest wall features (e.g., gynecomastia)
Characteristic physical findings in the chest in chronic liver disease include gynecomastia (tender and firm enlarged breast bud) and loss of secondary sexual hair in men, and breast atrophy in women.
dyspnea
Dyspnea on exertion is an uncommon symptom associated with pulmonary complications of portal hypertension. In patients with hepatopulmonary syndrome, platypnea and orthodeoxia are classically described; patients may also develop clubbing and cyanosis. Dyspnea may occur with hepatic hydrothorax.
chest pain
May occur in portopulmonary hypertension.
syncope
May occur in portopulmonary hypertension.
Risk factors
strong
alcohol misuse
intravenous drug use
unprotected intercourse
obesity
country of birth
Hepatitis B and C are endemic in certain global regions.[32]
weak
blood transfusion
Hepatitis B or C, both of which are known causes of cirrhosis, may be contracted from contaminated blood products, although this risk is extremely small due to the routine screening of blood donors and products for viral hepatitides.[30][31] Blood transfusion before 1992, or clotting factor transfusion before 1987, are risk factors in the US.
tattooing
Tattooing is a risk factor when universal precautions are not adequately observed.[33] Patients should be counseled about this.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer