Tests
1st tests to order
plasma potassium
Test
Plasma potassium is low in approximately 20% of patients with primary aldosteronism.[31]
Precautions must be taken to avoid false elevations of potassium that mask hypokalemia. The following are recommended:[72]
Avoiding fist clenching and releasing the tourniquet after venipuncture has been achieved.
Waiting for at least 10 seconds before gently withdrawing blood.
Using a syringe and needle rather than a Vacutainer, so that blood can be withdrawn in a slow and careful manner, and then gently discharged down the side of the opened sample tube.
Measuring potassium in plasma rather than serum.
Separating the plasma from the cells within 30 minutes of collection.
Result
normal or low
aldosterone/renin ratio
Test
This is the most reliable available screening test.[10][28][41][70]
A gray zone exists in ratios between 20 and 35. Some regard a ratio of >20 in combination with a plasma aldosterone concentration of >15 nanograms/dL as a positive screen.[39] This approach, however, will miss some patients with primary aldosteronism (more than one third in one series), including those with aldosterone-producing adenoma (one-fifth) who have lower plasma aldosterone levels.[27]
Diuretics should be ceased for at least 6 weeks and other interfering medications for at least 2 (and preferably 4) weeks before measuring the ratio, substituting other medications that have a lesser effect on results, such as verapamil slow-release (plus or minus hydralazine), prazosin, and moxonidine, in order to maintain hypertension control.[6][71][72][86]
Hypokalemia should be corrected and the patient should be encouraged to follow a liberal salt diet before ratio measurement.
Because of the effects of posture and time of day, sensitivity of the ratio is maximized by collecting blood midmorning from seated patients who have been upright (sitting, standing, or walking) for 2 to 4 hours.[6][71][72]
The ratio should be regarded as a screening test only, and should be measured more than once (serially if conditions of sampling, including medications, are being altered) before deciding whether to go on to a suppression test to definitively confirm or exclude the diagnosis.
Renin can be measured in terms of its enzymatic activity (plasma renin activity, PRA) or its mass (direct active renin concentration, DAR). PRA gives a better reflection of angiotensin II levels, and is less likely to give misleading results in the face of changes in substrate (angiotensinogen) concentrations (e.g., due to the menstrual cycle or due to treatment with female hormones for contraceptive or postmenopausal hormone replacement purposes).[80][81][108]
Automated immunometric assays for measuring DAR have been widely adopted as they are faster and more convenient than PRA. However, considerable work is required to validate and improve these methods to an acceptable standard. In the meantime, PRA remains the preferred approach.
Result
ratio is alternatively >70 for aldosterone in picomol/L and direct active renin concentration in mU/L; ratio >20 for plasma aldosterone in nanograms/100 mL and plasma renin activity in nanograms/mL/hour
Tests to consider
fludrocortisone suppression test
Test
Considered the most reliable means of definitively confirming or excluding PA.[6][7][28][71] Performed as an inpatient so that potassium can be monitored several times a day.
Upright (10 a.m.) plasma aldosterone is measured at the conclusion of 4 days' administration of fludrocortisone acetate (0.1 mg every 6 hours), slow-release sodium chloride (slow Na, 30 mmol 3 times daily with meals), and sufficient dietary salt to maintain a urinary excretion rate of at least 3 mmol sodium/kg/day.
Regarded as diagnostic of primary aldosteronism, provided that on day 4 all of the following 3 are present:[6][7][71]
Upright plasma renin activity is suppressed (<1 ng/mL/hour).
Plasma cortisol levels are lower at 10 a.m. than at 7 a.m., thereby excluding an acute adrenocorticotropic hormone rise, which may have prevented aldosterone suppression.
Plasma potassium is in the normal range, achieved by giving sufficient slow-release potassium chloride every 6 hours to keep levels (measured 3 to 4 times daily) close to 4.0 mEq/L.
Result
failure of upright (10 a.m.) plasma aldosterone to suppress to <6 ng/100 mL
saline infusion testing
Test
An alternative method to fludrocortisone suppression testing for definitively confirming or excluding primary aldosteronism.[37][87][88][89]
Usually performed with the patient supine; provided a bed is available, an outpatient visit will suffice. Reported to lack sensitivity, however, more sensitive if performed with the patient upright (seated).[90]
Plasma aldosterone is measured at the conclusion of an intravenous infusion of 0.9% saline (usually 2 L over 2-4 hours).
Result
plasma aldosterone (measured at the end of the infusion) is regarded as diagnostic, but the required level has varied from >5 to >10 ng/100 mL
oral salt loading
Test
An alternative method to fludrocortisone suppression testing for definitively confirming or excluding primary aldosteronism, but there are potential problems related to completeness of urine collection and accuracy and interpretation of urinary aldosterone measurements.[37]
Urinary aldosterone level is measured on third day of oral salt loading (sufficient to achieve a urine sodium excretion >200 mEq/day, with enough potassium supplementation to maintain normokalemia).
Result
24-hour urinary aldosterone level >12 micrograms/day
genetic testing
Test
The genetic defect in familial hyperaldosteronism type I (FH-I) is a "hybrid gene".[91] Testing was initially performed in specialized genetic laboratories using a Southern blot.[45] A more rapid long-PCR-based approach is now more widely available.[91] In patients with early onset primary aldosteronism who test negative for the hybrid gene, consideration should be given for genetic testing for mutations in KCNJ5, CACNA1H, and CLCN2.
Result
positive for hybrid gene in patients with FH-I
adrenal CT
Test
Detects almost all aldosterone-producing adrenocortical carcinomas (because of their usual large size), but misses approximately 50% of aldosterone-producing adenomas, and can be misleading by demonstrating nonfunctioning nodules either in the gland contralateral to one containing an aldosterone-producing adenoma or in a patient with bilateral adrenal hyperplasia.[6][71][109]
Important for detecting adrenal lesions that warrant consideration for removal based on their size alone (and hence their malignant potential; e.g., those of at least 2.5 cm).
Useful for localizing adrenal veins, which facilitates successful catheterization during subsequent adrenal venous sampling.[6][101][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CT showing lesion in right adrenal gland in patient with right aldosterone-producing adenomaFrom the personal collection of Dr Michael Stowasser; used with permission [Citation ends].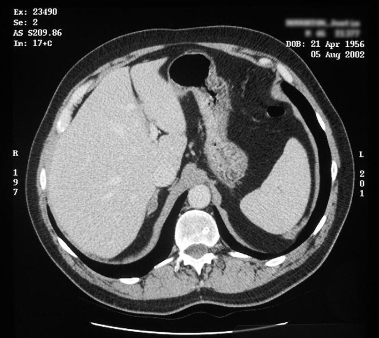 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CT showing lesion in right adrenal gland in patient with bilateral adrenal hyperplasiaFrom the personal collection of Dr Michael Stowasser; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CT showing lesion in right adrenal gland in patient with bilateral adrenal hyperplasiaFrom the personal collection of Dr Michael Stowasser; used with permission [Citation ends].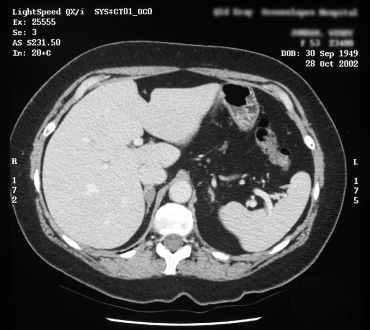
Result
detection of adrenal mass lesion
adrenal venous sampling
Test
Adrenal venous sampling (AVS) by an experienced radiologist is recommended when surgical treatment is feasible and desired by the patient to differentiate unilateral from bilateral adrenal disease.[28][70] Some guidelines suggest that AVS may be bypassed in patients ages <35 years with unilateral adenoma before proceeding to unilateral adrenalectomy.[10][28][41]
To avoid effects of posture and diurnal variation on steroid levels, sampling should be performed in the morning after overnight recumbency. Stress should be avoided and any venous catheterization should be delayed until the start of the procedure.
An adrenal vein to peripheral vein or low IVC cortisol gradient of at least 3.0 (at least 5.0 if adrenocorticotropic hormone stimulation is used) indicates successful catheterization. Calculation of the aldosterone/cortisol ratio for each adrenal and peripheral (or IVC) venous sample corrects for differences in dilution of adrenal with nonadrenal venous blood and is essential for interpretation.
If the aldosterone/cortisol ratio on one side is significantly higher (>2 times higher) than the simultaneous peripheral venous ratio, with a ratio no higher than peripheral on the other side, the study is considered to show lateralization, indicating that unilateral adrenalectomy should cure or significantly improve the hypertension.
Aldosterone levels (uncorrected for cortisol) measured on the side of the suppressed, normal gland are always higher than peripheral due to effects of adrenocorticotropic hormone and potassium, and can thereby give the mistaken impression of bilateral adrenal autonomous aldosterone production.[6][71][101][110]
In the uncommon circumstance that a patient with primary aldosteronism is also suspected of having autonomous adrenal cortisol overproduction based on overnight dexamethasone suppression testing, consideration should be given to using metanephrine (rather than cortisol) to gauge success of adrenal venous catheterization and to correct aldosterone levels for differences in dilution of adrenal venous blood.[111][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Adrenal venous sampling results from patient with left aldosterone-producing adenomaFrom the personal collection of Dr Michael Stowasser; used with permission [Citation ends].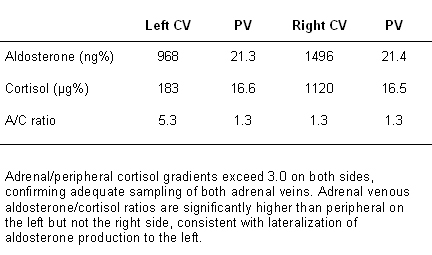
Result
aldosterone production lateralizes to one adrenal in unilateral forms (e.g., aldosterone-producing adenoma (APA) or carcinoma, unilateral adrenal hyperplasia); production is bilateral in bilateral forms (usually bilateral adrenal hyperplasia but also bilateral APAs)
adrenal MRI
Test
As with CT, can miss smaller aldosterone-producing adenomas and can be misleading by demonstrating nonfunctioning nodules either in the gland contralateral to one containing an aldosterone-producing adenoma or in a patient with bilateral adrenal hyperplasia.[96][109][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Aldosterone-producing adenomaFrom the personal collection of Dr Michael Stowasser; used with permission [Citation ends].
Result
detection of adrenal mass lesion
posture stimulation testing
Test
Plasma aldosterone measured at 7 a.m. or 8 a.m. following overnight recumbency and again at 10 a.m. after 2 to 3 hours of upright posture (sitting, standing, or walking).[97][99][100]
Result
plasma aldosterone responsive (rises by at least 50% over basal) in angiotensin II-responsive aldosterone-producing adenoma and in most cases of bilateral adrenal hyperplasia (BAH); unresponsive in angiotensin II-unresponsive aldosterone-producing adenoma, in familial hyperaldosteronism type I, and in some cases of BAH
angiotensin II infusion testing
Test
Plasma aldosterone is measured basally and 60 minutes after commencement of an intravenous infusion of angiotensin II, given at a rate of 2 nanograms/kg/minute in the early morning following overnight recumbency.[98][99][100]
Result
plasma aldosterone responsive (rises by at least 50% over basal) in angiotensin II-responsive aldosterone-producing adenoma and in most cases of bilateral adrenal hyperplasia (BAH); unresponsive in angiotensin II-unresponsive aldosterone-producing adenoma, in familial hyperaldosteronism type I, and in some cases of BAH
24-hour urinary hybrid steroids (18-hydroxy- and 18-oxo-cortisol)
dexamethasone suppression testing
Test
Measure serum cortisol and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) at 8 a.m. to 9 a.m. Repeat serum cortisol at 8 a.m. to 9 a.m. the following day after administering dexamethasone at 11 p.m.
Result
failure of serum cortisol to suppress to <2 micrograms/100 mL, accompanied by a low basal (predexamethasone) ACTH, suggests concomitant autonomous adrenal overproduction of cortisol
Emerging tests
¹¹ C-Metomidate PET/CT
Test
Nuclear imaging using PET-CT with labelled metomidate as a ligand of CYP11B1 and CYP11B2 has been proposed to be a viable alternative to adrenal vein sampling, or as an adjunct to AVS in difficult cases.[105][106]
Result
detection of unilateral isotope uptake in patients with aldosterone-producing adenoma
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer