Tests
1st tests to order
CBC
Test
Ordered routinely. Test is nonsensitive and nonspecific. It does not exclude diagnosis if normal.
WBC may be as high as 30,000 to 50,000/mm³ in fulminant colitis.
Result
WBC increased
stool guaiac (fecal occult blood test)
Test
Performed routinely to exclude other differential diagnoses. Results are often positive, but positive result is not specific for diagnosis.
Result
positive for occult blood
stool polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
Test
Recommended as sole investigation if hospital and laboratory personnel agree on the following stool submission criteria: unexplained, new-onset diarrhea (defined as 3 or more unformed stools in 24 hours) in patients who are not receiving laxatives in the last 48 hours.[2]
Recommended as part of multistep algorithm if there are no pre-agreed institutional criteria for patient stool submission.[2][73]
Highly sensitive with low/moderate specificity.
Do not perform repeat testing within 7 days during the same episode of diarrhea, and do not order tests for asymptomatic patients.[2][70][71][72]
Result
positive
stool immunoassay for glutamate dehydrogenase
Test
Detects the presence of Clostridioides difficile in the bowel, although it does not provide confirmation of infection.
Recommended as part of multistep algorithm if there are no pre-agreed institutional criteria for patient stool submission.[2][73]
Has high sensitivity and specificity for the diagnosis of C difficile infection.[76]
Result
positive
stool immunoassay for toxins A and B
Test
Recommended as part of multistep algorithm if there are no pre-agreed institutional criteria for patient stool submission.[2][73]
Results available within a few hours with sensitivity of 65% to 85% and specificity of 95% to 100%.[3]
Can be repeated up to 3 times to improve sensitivity, although evidence for repeat enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) testing has not been conclusive.[77]
Enzyme immunoassays detect toxin A, toxin B, or both A and B. Most laboratories perform a toxin B-only or toxin A and B assay due to concerns over toxin A-negative and B-positive strains causing disease.[74]
Result
positive
abdominal x-ray
Test
Ordered if there is significant abdominal distension.
Result
air in bowel, colonic dilation
Tests to consider
cell culture cytotoxicity neutralization assay
CT abdomen
Test
Indicated in patients with abdominal distension, worsening pain, or absent bowel sounds.
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CT scan of the abdomen showing gross thickening of the large bowel wall and obliteration of the lumenYates B, Murphy CM, et al. Pseudomembranous colitis in four patients with cystic fibrosis following lung transplantation. BMJ Case Reports. 2009; doi: 10.1136/bcr.11.2008.1218 [Citation ends].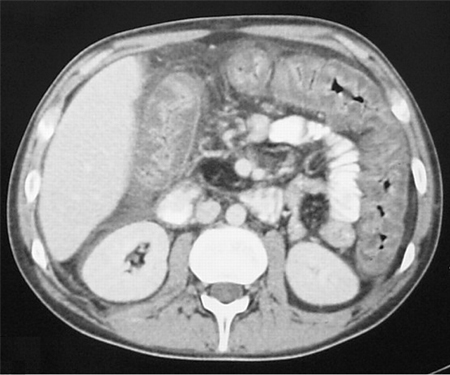 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CT scan of the abdomen showing diffuse bowel thickening suggestive of colitisFrom the collection of Dr Ali Hassoun [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CT scan of the abdomen showing diffuse bowel thickening suggestive of colitisFrom the collection of Dr Ali Hassoun [Citation ends].
Result
colonic dilation and diffuse colonic thickening
sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy
Test
Ulcerations and pseudomembrane formation are diagnostic but may be absent.
Result
colonic pseudomembrane and colitis
Emerging tests
stool lactoferrin or calprotectin
Test
Fecal biomarkers are increasingly being used to distinguish between inflammatory causes of diarrhea and non-inflammatory causes. There is insufficient evidence to recommend the use of these biomarkers in the diagnosis of C difficile infection at this time.[2]
Result
elevated
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer