Differentials
Common
Pharyngitis
History
throat pain and odynophagia worsening over several days; associated with fever and malaise
Exam
erythema, edema and/or exudates of the pharynx; tonsillar hypertrophy may cause severe narrowing of the pharynx; lymphadenopathy of the neck is often present
1st investigation
- rapid antigen test for group A Streptococcus (GAS):
positive in GAS infection
- CBC:
elevated WBC count
Other investigations
- culture of throat swab:
growth of causative organism
Esophageal candidiasis
History
dysphagia or odynophagia for liquids and/or solids; may be asymptomatic; history of corticosteroid, antibiotic, or inhaler use; history of an immunocompromised state
Exam
creamy white or yellowish plaques (thrush) in oropharynx or hypopharynx; may be normal exam
1st investigation
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy:
visualization of typical lesions of Candida
Other investigations
- biopsy of lesion:
histology characteristic Candida yeast forms in tissue and culture confirmation of the presence of Candida species
More
Stroke
History
progressive oropharyngeal dysphagia; coughing, choking, drooling, and regurgitation when swallowing liquids or solid food; dysarthria; limb weakness or fatigability
Exam
paraplegia, aphasia, dysarthria, vertigo, staggering, diplopia, deafness
1st investigation
- bedside swallowing assessment:
deglutitive coughing, choking, or nasal regurgitation
- modified barium swallow:
inability or excessive delay in initiation of pharyngeal swallowing, aspiration, nasopharyngeal regurgitation, food or liquid residue within the pharyngeal cavity after swallowing
- CT head without contrast:
hemorrhage or ischemia
Other investigations
- esophageal manometry:
unlike modified barium swallow this allows for quantification of contractile forces, intrabolus pressure, detection of upper esophageal sphincter relaxation, and coordination of pharyngeal contraction
Muscle tension dysphagia
History
throat discomfort, food/pills sticking, throat tightness, difficulty swallowing
Exam
laryngeal hypersensitivity, laryngeal inflammation
1st investigation
- none:
no single, specific investigation as usually a diagnosis of exclusion is made with speech therapists rather than with conventional testing
Other investigations
Diffuse esophageal spasm
History
recurrent chest pain indistinguishable from cardiac chest pain and is relieved by nitroglycerin, associated with meals but rarely exertionally induced, dysphagia is intermittent and nonprogressive
Exam
no specific physical findings
1st investigation
- esophageal manometry:
simultaneous and repetitive contractions of esophageal body with normal lower esophagus sphincter relaxation
Other investigations
- barium esophagogram:
classic finding of "corkscrew" esophagus
Gastroesophageal reflux
History
heartburn, acid regurgitation, dysphagia
Exam
no specific physical findings
1st investigation
- therapeutic trial of proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs):
relief of symptoms
More
Hiatal hernia
History
symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease: for example, reflux, regurgitation; bleeding, dysphagia
Exam
no specific physical findings
1st investigation
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy:
the diaphragmatic hiatus is easily visualized in retroflexed view[74]
Other investigations
- upper gastrointestinal barium series:
herniation of stomach through the esophageal hiatus
Postoperative cervical spine surgery
History
swallowing difficulties immediately after cervical spine surgery
Exam
anterior operative neck incision
1st investigation
- video swallow study, modified barium swallow:
may demonstrate anterior displacement of the posterior pharyngeal wall diverting solids and liquids because of inflammation or from the plate itself; scarring or inflammation of the posterior pharyngeal wall may impair laryngeal/pharyngeal elevation with each swallow, thereby impeding epiglottic flexion and cricopharyngeal opening[76]
Other investigations
- CT/MRI cervical spine:
edema of posterior pharyngeal wall and prevertebral space, indentation of posterior pharyngeal wall by cervical spine plate
Uncommon
Epiglottitis
History
progressive sore throat; difficulty swallowing over the course of 1-2 days; unable to control secretions; may be life-threatening as it progresses because of airway compromise; faster progression in children than in adults
Exam
patient may be in “sniff” position (whereby the body leans forward and the head and neck are tilted forward and upward); muffled voice; neck lymphadenopathy
1st investigation
- flexible laryngoscopy:
swelling of supraglottic structures
Other investigations
- lateral neck x-ray:
markedly enlarged epiglottis
More
Retropharyngeal abscess
History
dysphagia for solids and liquids, odynophagia, fever, chills, hoarseness, pain with head turning
Exam
pharyngitis, lymphadenopathy, nuchal rigidity may be present; exam may be surprisingly benign with symptoms seemingly out of proportion to findings
1st investigation
- CT neck with contrast:
enhancing retropharyngeal abscess
Other investigations
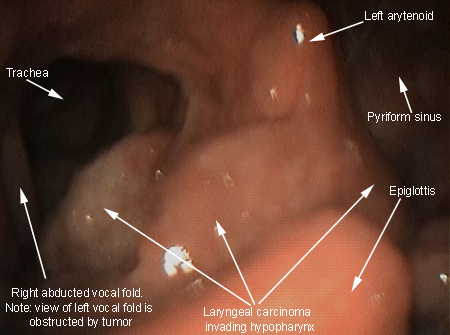
Oropharyngeal carcinoma (squamous cell carcinoma) and metastases
History
odynophagia, weight loss, chronic cough, hemoptysis, stridor, neck mass, hoarseness; history of smoking and alcohol consumption as risk factors for squamous cell carcinoma
Exam
metastatic cervical lymph nodes or physical findings of the primary sites such as breast, lung, and colon cancer
1st investigation
- flexible nasopharyngoscopy/laryngoscopy:
visualization of tumor
More
Other investigations
- CT neck with contrast:
determines submucosal extent of the tumor and nonpalpable adenopathy
Zenker diverticulum
History
typically asymptomatic, but patients can report intermittent solid food dysphagia, regurgitation of undigested food, halitosis, excessive salivation, cough
Exam
no specific physical findings
1st investigation
Other investigations
Cricopharyngeal bar
History
delayed swallow initiation, solid food dysphagia, excessive post-swallow residue, sensation of a bolus holding up in the neck, repeated swallowing, coughing, and choking
Exam
no specific physical findings
1st investigation
- barium swallow:
compression effect of the cricopharyngeal bar
Other investigations
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy:
pooling of secretions in the pharynx
More - manometry:
high upper esophageal pressure
Thyromegaly (goiter)
History
solid food dysphagia, excessive post-swallow residue, sensation of a bolus holding up in the neck, repeated swallowing, coughing, and choking, symptoms of hypo- or hyperthyroidism
Exam
enlarged thyroid
1st investigation
- barium swallow:
compression effect of enlarged thyroid
Other investigations
- thyroid function tests:
thyroid-stimulating hormone low, elevated free T4
- neck ultrasound or CT scan:
determines size and location of goiter
Cervical lymphadenopathy
History
delayed swallow initiation, solid food dysphagia, nasopharyngeal regurgitation, excessive post-swallow residue, sensation of a bolus holding up in the neck, repeated swallowing, coughing, and choking
Exam
lymphadenopathy
1st investigation
- CT scan of neck or chest:
enlarged lymph node compressing esophagus
Other investigations
- barium swallow:
compression effect of the underlying disease
Oropharyngeal stenosis
History
history of radiation or surgery on head and neck
Exam
no specific physical findings
1st investigation
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy:
stenosis or stricture
Other investigations
- videofluoroscopy:
functional impairment of the swallowing mechanism
Parkinson disease
History
progressive oropharyngeal dysphagia, coughing, choking, drooling, and regurgitation when swallowing liquids or solid food; tremor, bradykinesia
Exam
masked facies, cogwheel rigidity, decreased spontaneous eye blink rate, slurred/mumbled speech, hypokinetic, excess saliva, shuffling, short-stepped gait
1st investigation
- bedside swallowing assessment:
deglutitive coughing, choking, or nasal regurgitation
- modified barium swallow:
inability or excessive delay in initiation of pharyngeal swallowing, aspiration, nasopharyngeal regurgitation, residue of food or liquid within the pharyngeal cavity after swallowing
Other investigations
- esophageal manometry:
unlike modified barium swallow this allows for quantification of contractile forces, intrabolus pressure, detection of upper esophageal sphincter relaxation, and coordination of pharyngeal contraction
Vocal cord paralysis
History
hoarseness, aspiration symptoms with thin liquids, weak, ineffective cough; prior history of thyroid, cervical spine, lung or skull base surgery; history of lung, mediastinal or esophageal tumors
Exam
weak, breathy voice
1st investigation
- laryngoscopy:
immobile vocal cord
Other investigations
Multiple sclerosis
History
progressive oropharyngeal dysphagia, coughing, choking, drooling, and regurgitation when swallowing liquids or solid food; diplopia, urinary retention, hesitancy or frequency, urinary tract infections, constipation, fatigue, vision loss in one eye
Exam
hemiparesis, cognitive problems, optic neuritis
1st investigation
- bedside swallowing assessment:
deglutitive coughing, choking, or nasal regurgitation
- modified barium swallow:
inability or excessive delay in initiation of pharyngeal swallowing, aspiration, nasopharyngeal regurgitation, residue of food or liquid within the pharyngeal cavity after swallowing
- brain MRI:
demyelination perpendicular to the lateral ventricles and corpus callosum
Other investigations
- esophageal manometry:
unlike modified barium swallow this allows for quantification of contractile forces, intrabolus pressure, detection of upper esophageal sphincter relaxation, and coordination of pharyngeal contraction
- cerebrospinal fluid analysis:
oligoclonal bands
Myasthenia gravis
History
progressive oropharyngeal dysphagia, coughing, choking, drooling, and regurgitation when swallowing liquids or solid food; weakness worsened by fatigue, stress, and exertion
Exam
ptosis, muscle weakness
1st investigation
- bedside swallowing assessment:
deglutitive coughing, choking, or nasal regurgitation
- modified barium swallow:
inability or excessive delay in initiation of pharyngeal swallowing, aspiration, nasopharyngeal regurgitation, residue of food or liquid within the pharyngeal cavity after swallowing
- edrophonium chloride (brand: Tensilon) test:
progressive weakening with repetitive muscle stimulation
Other investigations
- esophageal manometry:
unlike modified barium swallow this allows for quantification of contractile forces, intrabolus pressure, detection of upper esophageal sphincter relaxation, and coordination of pharyngeal contraction
- acetylcholine receptor antibody assays:
positive
Sjogren syndrome
History
dry eyes, dry mouth (xerostomia); difficulty initiating swallow and transferring the food bolus into the pharynx; food sticking in throat
Exam
lack of saliva with “parched” oral mucosa, which may stick to tongue blade on exam
1st investigation
- serum autoantibodies - anti-Ro (SS-A) and anti-La (SS-B):
positive
Other investigations
- Schirmer test:
decreased tear production (<5 mm in 5 minutes)
- salivary gland biopsy:
mononuclear cell infiltrates (B and T cells and dendritic cells) in perivascular or periductal areas of sampled gland
Scleroderma
History
dysphagia to both solids and liquids, heartburn, history of Raynaud syndrome
Exam
calcinosis, sclerodactyly, telangiectasia
1st investigation
- esophageal manometry:
low-amplitude or absent contraction in distal esophagus, with low lower esophagus sphincter pressure
Other investigations
- serum anti-DNA topoisomerase I (Scl-70), antinuclear antibodies and anti-centromere antibodies:
positive
Inflammatory myopathies
History
progressive oropharyngeal dysphagia, coughing, choking, drooling, and regurgitation when swallowing liquids or solid food; proximal muscle weakness
Exam
symmetrical proximal muscle weakness
1st investigation
- bedside swallowing assessment:
deglutitive coughing, choking, or nasal regurgitation
- modified barium swallow:
inability or excessive delay in initiation of pharyngeal swallowing, aspiration, nasopharyngeal regurgitation, residue of food or liquid within the pharyngeal cavity after swallowing
- serum creatine phosphokinase:
elevated
- electromyography:
evidence of myopathy
Other investigations
- esophageal manometry:
unlike modified barium swallow this allows for quantification of contractile forces, intrabolus pressure, detection of upper esophageal sphincter relaxation, and coordination of pharyngeal contraction
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
History
progressive oropharyngeal dysphagia, coughing, choking, drooling, and regurgitation when swallowing liquids or solid food; muscle weakness
Exam
pathologic hyperreflexia, spasticity, extensor plantar response, weakness, muscle atrophy, fasciculations, and cramps
1st investigation
- bedside swallowing assessment:
deglutitive coughing, choking, or nasal regurgitation
- modified barium swallow:
inability or excessive delay in initiation of pharyngeal swallowing, aspiration, nasopharyngeal regurgitation, residue of food or liquid within the pharyngeal cavity after swallowing
Other investigations
- esophageal manometry:
unlike modified barium swallow this allows for quantification of contractile forces, intrabolus pressure, detection of upper esophageal sphincter relaxation, and coordination of pharyngeal contraction
Progressive supranuclear palsy
History
progressive oropharyngeal dysphagia, coughing, choking, drooling, and regurgitation when swallowing liquids or solid food; falls, balance impairment
Exam
supranuclear ophthalmoplegia, dysarthria, gait impairment
1st investigation
- bedside swallowing assessment:
deglutitive coughing, choking, or nasal regurgitation
Other investigations
- modified barium swallow:
inability or excessive delay in initiation of pharyngeal swallowing, aspiration, nasopharyngeal regurgitation, residue of food or liquid within the pharyngeal cavity after swallowing
- esophageal manometry:
unlike modified barium swallow this allows for quantification of contractile forces, intrabolus pressure, detection of upper esophageal sphincter relaxation, and coordination of pharyngeal contraction
Wilson disease
History
progressive oropharyngeal dysphagia, coughing, choking, drooling, and regurgitation when swallowing liquids or solid food; bradykinesia, personality or behavioral changes
Exam
tremor, rigidity, psychosis, Kayser-Fleischer ring
1st investigation
- bedside swallowing assessment:
deglutitive coughing, choking, or nasal regurgitation
- liver enzymes:
elevated
Other investigations
- modified barium swallow:
inability or excessive delay in initiation of pharyngeal swallowing, aspiration, nasopharyngeal regurgitation, residue of food or liquid within the pharyngeal cavity after swallowing
- esophageal manometry:
unlike modified barium swallow this allows for quantification of contractile forces, intrabolus pressure, detection of upper esophageal sphincter relaxation, and coordination of pharyngeal contraction
- serum ceruloplasmin level:
<30 mg/dL
- 24-hour urinary copper:
>100 micrograms
- slit-lamp examination:
Kayser-Fleischer (KF) rings
More
Tardive dyskinesia
History
progressive oropharyngeal dysphagia, coughing, choking, drooling, and regurgitation when swallowing liquids or solid food; long-term antipsychotic drug use
Exam
chorea of the lips, tongue, face, and neck
1st investigation
- bedside swallowing assessment:
deglutitive coughing, choking, or nasal regurgitation
Other investigations
- modified barium swallow:
inability or excessive delay in initiation of pharyngeal swallowing, aspiration, nasopharyngeal regurgitation, residue of food or liquid within the pharyngeal cavity after swallowing
- esophageal manometry:
unlike modified barium swallow this allows for quantification of contractile forces, intrabolus pressure, detection of upper esophageal sphincter relaxation, and coordination of pharyngeal contraction
Idiopathic achalasia
History
dysphagia of solids more than liquids; patients may eat slowly, raise their arms or arch their back to aid symptoms; difficulty belching; chest pain; regurgitation; weight loss
Exam
no specific physical findings
1st investigation
- esophageal manometry:
aperistalsis of esophageal body, low-amplitude simultaneous contractions after swallow, absent or incomplete lower esophagus sphincter relaxation with swallow
More
Other investigations
- timed barium esophagogram:
loss of primary peristalsis in distal esophagus, poor emptying, dilated esophagus or sigmoid tortuosity, and presence of "bird's beak"
- chest CT scan:
excludes external compression (secondary achalasia)
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy:
differentiates idiopathic achalasia from secondary causes of achalasia such as gastroesophageal junction tumors
Nutcracker esophagus
History
chest pain, less frequently dysphagia
Exam
no specific physical findings
1st investigation
- esophageal manometry:
high-amplitude peristalsis ≥180 mmHg
Other investigations
Caustic agents
History
oral burns, sore throat, odynophagia, hoarseness, dysphagia, chest pain, back pain
Exam
tongue edema and ulceration, drooling, stridor, aphonia
1st investigation
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy:
area of burn in acute setting; stricture or narrowing of the lumen in chronic setting
More
Other investigations
- fiberoptic nasopharyngolaryngoscopy:
area of burn
- CXR:
subcutaneous emphysema, pulmonary infiltrate, pneumothorax, pneumomediastinum
- barium swallow with Gastrografin:
perforation in acute setting; narrowing of lumen in chronic setting
Pill-induced injury
History
ingestion of doxycycline, quinidine, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, iron, alendronate; sensation of pill sticking in the throat, chest pain, odynophagia, progressive solid dysphagia
Exam
no specific physical findings
1st investigation
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy:
ulcer formation, plaques resembling Candida, strictures
Other investigations
Radiation exposure
History
history of radiation to neck and chest
Exam
woody induration of neck, discoloration of skin
1st investigation
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy:
stricture or narrowing of the lumen[73]
Other investigations
- barium esophagogram:
narrowing of the lumen
Esophageal carcinoma
History
symptoms of reflux in early disease, progressive dysphagia to solids, odynophagia, iron deficiency, hoarseness, weight loss; history of tobacco/alcohol use, achalasia, caustic injury, human papillomavirus (HPV) for squamous cell carcinoma, gastroesophageal reflux disease, Barrett esophagus
Exam
cervical lymphadenopathy
1st investigation
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy:
mass could be ulcerated
Other investigations
- barium esophagogram:
filling defect
Foreign body
History
solid food dysphagia, odynophagia, foreign body sensation, excessive secretions, difficulty breathing, asphyxiation
Exam
respiratory distress
1st investigation
Other investigations
Benign esophageal tumors (leiomyoma, lipoma, polyps)
History
solid food dysphagia
Exam
no specific physical findings
1st investigation
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy:
esophageal lesion
Other investigations
Esophageal metastases
History
progressive dysphagia to solids, odynophagia, weight loss, anorexia, history of cancer
Exam
no specific physical findings
1st investigation
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy:
ulcerated lesion or mass
Other investigations
Esophageal compression
History
progressive solid food dysphagia, osteoarthritis
Exam
neck masses, lymph nodes, signs of osteoarthritis
1st investigation
- barium swallow:
local narrowing of lumen
Other investigations
- chest CT scan:
mediastinal mass or lymph node compressing the esophagus
- cervical x-ray:
osteoarthritis
Schatzki ring
History
intermittent solid food dysphagia, food impaction
Exam
no specific physical findings
1st investigation
- barium swallow:
circumferential filling defect near gastroesophageal junction
Other investigations
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy:
ring present near gastroesophageal junction
Gastroesophageal muscular ring
History
usually asymptomatic
Exam
no specific physical findings
1st investigation
- barium swallow:
circumferential filling defect near gastroesophageal junction
Other investigations
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy:
ring proximal to gastroesophageal junction[27]
Esophageal diverticulum
History
intermittent solid food dysphagia, chest pain, regurgitation of undigested food, halitosis, excessive salivation
Exam
no specific physical findings
1st investigation
- barium swallow:
diverticulum
Other investigations
Eosinophilic esophagitis
History
long-standing solid food dysphagia, usually going back to early childhood; history of congenital abnormalities and allergic conditions
Exam
no specific physical findings
1st investigation
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy:
multiple esophageal rings, often associated with an area of esophageal narrowing, white exudate/plaques, strictures[41][75]
- esophageal biopsies:
one of the three following pathologic findings: ≥15 intraepithelial eosinophils/high power field in at least one esophageal site; epithelial changes, such as basal layer hyperplasia and dilated intercellular spaces; altered eosinophil character with surface layering and abscesses[41] In the US, at least 2-4 biopsies are taken; at least 6 biopsies are recommended in Europe.[36][43][44]
Other investigations
Esophageal web
History
intermittent solid food dysphagia, aspiration, regurgitation
Exam
no specific physical findings
1st investigation
- barium swallow:
thin projection off anterior surface of postcricoid esophagus for webs
More
Other investigations
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy:
thin, eccentric lesion with normal-appearing mucosa compromising the esophageal lumen
Botulism
History
history of consumption of contaminated food, history of wound contamination, progressive oropharyngeal dysphagia, difficulty breathing, abdominal pain, vomiting, incoordination
Exam
signs of respiratory distress, fever, cranial nerve abnormalities
1st investigation
- bedside swallowing assessment:
deglutitive coughing, choking, or nasal regurgitation
- modified barium swallow:
inability or excessive delay in initiation of pharyngeal swallowing, aspiration, nasopharyngeal regurgitation, residue of food or liquid within the pharyngeal cavity after swallowing
Other investigations
- mouse bioassay for botulinum toxin:
positive
- culture of food samples, gastric aspirates, or fecal samples:
positive for botulinum toxin
Oral mucositis
History
chemotherapy, radiation, oral pain, xerostomia, diarrhea
Exam
erythema or ulceration of oral mucosa
1st investigation
- none:
diagnosis is clinical
Other investigations
Cervical osteophytes
History
neck arthritis, progressive neck stiffness, posterior neck pains
Exam
may be normal, or there may be limited neck extension, bulging posterior oropharyngeal, and/or hypopharyngeal wall
1st investigation
- lateral cervical spine x-ray:
large cervical osteophytes
- video swallow study, modified barium swallow:
will demonstrate anterior displacement of the posterior pharyngeal wall; depending on the location of the osteophyte, its presence may impair epiglottic closure of the laryngeal introitus or the oral intake may be diverted around the osteophyte increasing the risk of penetration and aspiration; large osteophytes pressing on the hypopharynx or cervical esophagus may impair solids (more than liquids) from passing through easily
More
Other investigations
- CT/MRI cervical spine:
protrusion of cervical osteophytes into oropharynx or hypopharynx
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer