Complications
If no improvement with nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic therapy, referral to an orthopedist should be considered.
Spinal stenosis may result from degenerative changes, typically in the lumbar spine but also in the cervical spine. Neurogenic claudication is characterized by back and leg pain, and the patient may complain of paresthesia in the lower limbs that is worse on walking and improved by sitting. A referral for orthopedic spinal opinion to consider decompression surgery is warranted.
Long-term use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) analgesia can cause gastric irritation, peptic ulceration, and upper gastrointestinal bleeding in some patients. This risk can be decreased with the use of proton-pump inhibitors.
[  ]
]
Arthrocentesis and corticosteroid injection, and/or referral to rheumatology, should be considered.
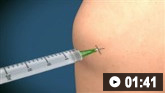
How to aspirate synovial fluid from the knee and administer intra-articular medication using a medial approach.
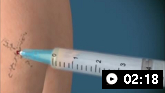
How to aspirate synovial fluid from the shoulder and administer intra-articular medication. Video demonstrates a posterior approach to the glenohumeral joint and a lateral approach to the subacromial space.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) analgesia decreases the production of renal prostaglandins, which act as vasodilators to maintain renal perfusion pressure. In a healthy person these prostaglandins have only a minor role, but they become progressively more important in people with glomerular disease and renal insufficiency. A resulting fall in hemodynamic pressure can cause acute renal failure.
NSAIDs may also cause acute interstitial nephritis as a result of decreased prostaglandin synthesis.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer