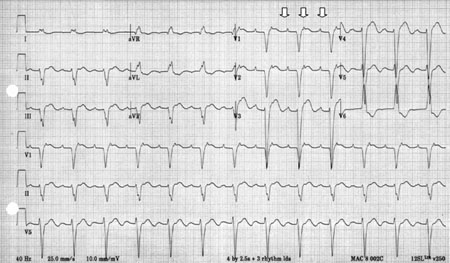
Summary
Definition
History and exam
Other diagnostic factors
- medications
- palpitations
- fatigue, weakness
- chest pain
- shortness of breath, cough
- nausea, vomiting
- lightheadedness, syncope
- rales
- edema
Risk factors
- substance misuse (alcohol ingestion/withdrawal, cocaine, amphetamines)
- digoxin toxicity
- previous cardiac surgery to correct congenital heart defects
- coronary artery disease
- exacerbation of chronic lung disease
- theophylline
Diagnostic tests
Tests to consider
- vagal maneuvers, adenosine
- thyroid-stimulating hormone
- echocardiogram
- ambulatory 24-hour (Holter) ECG or event recorder
- electrophysiologic study (EPS)
Treatment algorithm
Contributors
Authors
Danesh Kella, MBBS, FHRS
Assistant Professor
Department of Cardiovascular Diseases
Division of Heart Rhythm
Mayo Clinic
Jacksonville
FL
Disclosures
DK receives honoraria from Zoll Medical.
Acknowledgements
Dr Danesh Kella would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Sarah Stahmer, previous contributor to this topic.
Peer reviewers
Kathryn L. Berlacher, MD, MS
Assistant Professor and Cardiology Fellowship Program Director
University of Pittsburgh Medical Center
Pittsburgh
PA
Disclosures
KLB declares that she has no competing interests.
Mehak Dhande, MD
Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology Fellow
University of Pittsburgh Medical Center
Pittsburgh
PA
Disclosures
MD declares that she has no competing interests.
Amal Mattu, MD
Associate Professor of Emergency Medicine
University of Maryland Medical Center
Baltimore
MD
Disclosures
AM declares that he has no competing interests.
Vias Markides, MB(Hons), BS(Hons), MD, FRCP
Consultant Cardiologist
Royal Brompton & Harefield NHS Trust
Imperial College London
London
UK
Disclosures
VM declares that he has no competing interests.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer