Hepatitis A virus (HAV) infection is endemic in resource-limited countries.[1]Committee on Infectious Diseases, American Academy of Pediatrics; Kimberlin D, Barnett E, Lynfield R, et al. Hepatitis A. In: Red Book: 2021–2024 report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases. 32nd ed. Elk Grove Village, IL: American Academy of Pediatrics; 2021. In developed countries, outbreaks are associated with contaminated food or water. Men who have sex with men, people who use illegal drugs, people who experience homelessness, and people who travel to endemic areas are at higher risk of infection.[1]Committee on Infectious Diseases, American Academy of Pediatrics; Kimberlin D, Barnett E, Lynfield R, et al. Hepatitis A. In: Red Book: 2021–2024 report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases. 32nd ed. Elk Grove Village, IL: American Academy of Pediatrics; 2021.[5]Abutaleb A, Kottilil S. Hepatitis A: epidemiology, natural history, unusual clinical manifestations, and prevention. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2020 Jun;49(2):191-9.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7883407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32389358?tool=bestpractice.com
There are an estimated 1.4 million cases per year globally.[5]Abutaleb A, Kottilil S. Hepatitis A: epidemiology, natural history, unusual clinical manifestations, and prevention. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2020 Jun;49(2):191-9.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7883407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32389358?tool=bestpractice.com
High-prevalence areas include Africa and parts of Asia and Latin America.[6]Hodges M, Sanders E, Aitken C. Seroprevalence of hepatitis markers; HAV, HBV, HCV and HEV amongst primary school children in Freetown, Sierra Leone. West Afr J Med. 1998 Jan-Mar;17(1):36-7.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9643158?tool=bestpractice.com
[7]Sawayama Y, Hayashi J, Ariyama I, et al. A ten year serological survey of hepatitis A, B, and C viruses infections in Nepal. J Epidemiol. 1999 Nov;9(5):350-4.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10616269?tool=bestpractice.com
[8]Hau CH, Hien TT, Tien NT, et al. Prevalence of enteric hepatitis A and E viruses in the Mekong River delta region of Vietnam. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1999 Feb;60(2):277-80.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10072151?tool=bestpractice.com
[9]Arankalle VA, Tsarev SA, Chadha MS, et al. Age-specific prevalence of antibodies to hepatitis A and E viruses in Pune, India, 1982 and 1992. J Infect Dis. 1995 Feb;171(2):447-50.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7844387?tool=bestpractice.com
The majority of infections in these areas occur in early childhood; infections are often asymptomatic in children and reported incidence rates are low. In high-prevalence areas, adults are generally immune.
Regions of Southern and Eastern Europe and parts of the Middle East have intermediate prevalence.[10]Jacobsen KH, Wiersma ST. Hepatitis A virus seroprevalence by age and world region, 1990 and 2005. Vaccine. 2010 Sep 24;28(41):6653-7.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20723630?tool=bestpractice.com
Areas of low prevalence and very low prevalence include North America and Western Europe, where few people are infected in childhood and the majority of the population remains susceptible throughout adulthood.[10]Jacobsen KH, Wiersma ST. Hepatitis A virus seroprevalence by age and world region, 1990 and 2005. Vaccine. 2010 Sep 24;28(41):6653-7.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20723630?tool=bestpractice.com
[11]Beran J, Douda P, Rychly R. Seroprevalence of viral hepatitis in the Czech Republic. Eur J Epidemiol. 1999 Oct;15(9):805-8.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10608359?tool=bestpractice.com
[12]Beutels M, Van Damme P, Aelvoet W, et al. Prevalence of hepatitis A, B and C in the Flemish population. Eur J Epidemiol. 1997 Apr;13(3):275-80.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9258525?tool=bestpractice.com
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Geographic distribution of the prevalence of hepatitis A (based on summary of available data)CDC website; used with permission [Citation ends].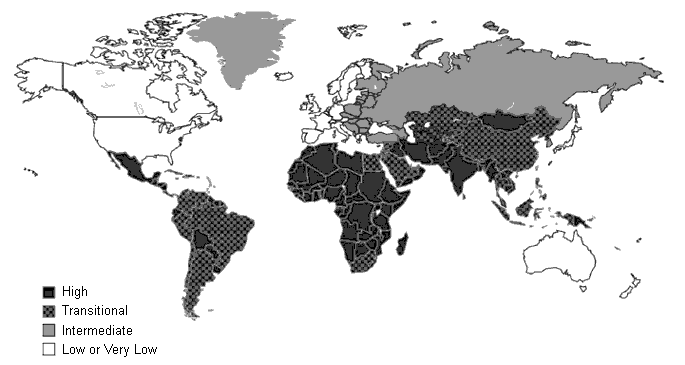
In the US, HAV infection continues to be one of the most frequently reported vaccine-preventable conditions.
An outbreak of HAV infection was seen in the US from 2015 to 2020. The cases started decreasing from 2020, and eight states declared the end of the outbreak in 2021. In 2021, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention received 11,500 reports of HAV infection from US states and territories, which is 4% higher than that in 2015 but 43% lower than that in 2020.[13]Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Viral hepatitis surveillance report - United States, 2021. Aug 2023 [internet publication].
https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/statistics/2021surveillance/hepatitis-a.htm
There have been an estimated 44,910 cases, 27,441 hospitalizations, and 423 deaths following HAV infection since the hepatitis A outbreaks were first identified in 2016.[14]Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Person-to-person outbreaks of hepatitis A across the United States. Nov 2023 [internet publication].
https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/outbreaks/2017March-HepatitisA.htm
In 2021, 3864 cases of hepatitis A were reported by 30 European Economic Area countries.[15]European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Hepatitis A - annual epidemiological report for 2021. Dec 2022 [internet publication].
https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/hepatitis-annual-epidemiological-report-2021
