In high-income countries, where Shigella sonnei is more endemic, Shigella usually presents as a mild, self-limited illness.[1]Center for Disease Control and Prevention. CDC Yellow Book 2024: health information for international travel. Section 5: travel-associated infections & diseases - shigellosis. Jun 2023 [internet publication].
https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/yellowbook/2024/infections-diseases/shigellosis
Medical help is not always sought, but confirmation of suspected diagnosis is usually made on the basis of stool cultures.[5]Gastrointestinal infections and food poisoning. In: Bannister BA, Gillespie SH, Jones J. Infection: microbiology and management. 3rd ed. Oxford, UK: Blackwell Publishing Ltd.; 2006:167-201.S flexneri causes a more severe illness and is more endemic in low- and middle-income countries.
History and clinical examination
Key risk factors include exposure to contaminated water or food, direct fecal-oral contact, age <5 years, malnutrition, poor hygiene and cramped conditions, and travel to endemic areas.[2]Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). National Shigella surveillance: Shigella annual report, 2016. 21 May 2018 [internet publication].
http://www.cdc.gov/nationalsurveillance/shigella-surveillance.html
[4]Kotloff KL, Winickoff JP, Ivanoff B, et al. Global burden of Shigella infections: implications for vaccine development and implementation of control strategies. Bull World Health Organ. 11999;77(8):651-66.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2557719/pdf/10516787.pdf
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10516787?tool=bestpractice.com
[5]Gastrointestinal infections and food poisoning. In: Bannister BA, Gillespie SH, Jones J. Infection: microbiology and management. 3rd ed. Oxford, UK: Blackwell Publishing Ltd.; 2006:167-201.[6]Kotloff KL, Riddle MS, Platts-Mills JA, et al. Shigellosis. Lancet. 2018 Feb 24;391(10122):801-12.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29254859?tool=bestpractice.com
[8]Schroeder GN, Hilbi H. Molecular pathogenesis of Shigella spp.: controlling host cell signaling, invasion, and death by type III secretion. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2008 Jan;21(1):134-56.
http://cmr.asm.org/content/21/1/134.full
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18202440?tool=bestpractice.com
[13]World Health Organization. Guidelines for the control of shigellosis, including epidemics due to Shigella dysenteriae type 1. 2005 [internet publication].
http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/43252/1/924159330X.pdf
[14]King CK, Glass R, Bresee JS, et al. Managing acute gastroenteritis among children: oral rehydration, maintenance, and nutritional therapy. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2003 Nov 21;52(RR-16):1-16.
http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/rr5216a1.htm
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14627948?tool=bestpractice.com
Diarrheal illness begins around 1-2 days after exposure.[1]Center for Disease Control and Prevention. CDC Yellow Book 2024: health information for international travel. Section 5: travel-associated infections & diseases - shigellosis. Jun 2023 [internet publication].
https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/yellowbook/2024/infections-diseases/shigellosis
The diarrhoea may initially be watery and profuse, but as the source is mostly colonic, it tends to be low volume.[5]Gastrointestinal infections and food poisoning. In: Bannister BA, Gillespie SH, Jones J. Infection: microbiology and management. 3rd ed. Oxford, UK: Blackwell Publishing Ltd.; 2006:167-201. There may be visible blood in the stool.[22]Shane AL, Mody RK, Crump JA, et al. 2017 Infectious Diseases Society of America clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of infectious diarrhea. Clin Infect Dis. 2017 Nov 29;65(12):e45-80.
https://academic.oup.com/cid/article/65/12/e45/4557073
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29053792?tool=bestpractice.com
Abdominal cramps, fever, and tenesmus are common. Although rare, young children may experience seizures.[23]Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Information for healthcare professionals: shigella-shigellosis. Dec 2023 [internet publication].
https://www.cdc.gov/shigella/audience-medical-professionals.html
Vomiting is uncommon.[22]Shane AL, Mody RK, Crump JA, et al. 2017 Infectious Diseases Society of America clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of infectious diarrhea. Clin Infect Dis. 2017 Nov 29;65(12):e45-80.
https://academic.oup.com/cid/article/65/12/e45/4557073
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29053792?tool=bestpractice.com
Shigella dysenteriaeand Sflexneri often cause a more severe illness, with fever and worsening bloody diarrhea with mucus. Meningism, or other signs of altered neurologic status, may indicate Shigella-induced encephalopathy.
Clinical examination may reveal signs of volume depletion due to poor oral intake; eating or drinking appears to exacerbate the cramping abdominal pain.[5]Gastrointestinal infections and food poisoning. In: Bannister BA, Gillespie SH, Jones J. Infection: microbiology and management. 3rd ed. Oxford, UK: Blackwell Publishing Ltd.; 2006:167-201. Lower abdominal tenderness may be present, along with normal or increased bowel sounds. Toxic dilation of the colon is a consideration, as Shigella may cause severe colitis.
Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) is a severe complication. Clinical findings in children such as somnolence (due to anemia) or dry diapers (due to anuria) should raise suspicion. Stool microscopy and culture are important first-line tests to determine the cause of HUS in order to guide treatment.
Stool tests
Shigellosis is diagnosed on the basis of history, clinical features, and stool cultures. The stool culture process is stepwise. The stool sample is suspended in MacConkey agar to identify non-lactose fermenters such as Shigella species.[5]Gastrointestinal infections and food poisoning. In: Bannister BA, Gillespie SH, Jones J. Infection: microbiology and management. 3rd ed. Oxford, UK: Blackwell Publishing Ltd.; 2006:167-201. More selective media are then used, after which slide agglutination with Shigella antisera further indicates the likelihood of shigellosis. Biochemical screening tests are confirmatory for species if non-lactose fermenters are found and thought likely to be Shigella on the basis of selective media cultures and slide agglutination. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Stool exudates in a patient with Shigella infectionCDC [Citation ends].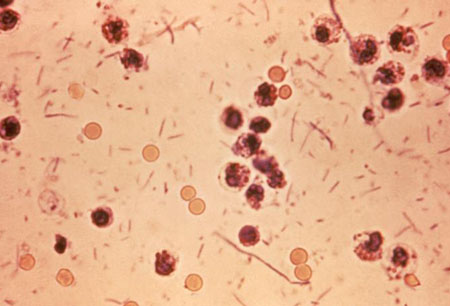
Shigella is a notifiable disease, and local laboratories should report confirmed cases to the appropriate public health departments or authorities.
CDC: national notifiable infectious diseases surveillance system
Opens in new window[13]World Health Organization. Guidelines for the control of shigellosis, including epidemics due to Shigella dysenteriae type 1. 2005 [internet publication].
http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/43252/1/924159330X.pdf
[22]Shane AL, Mody RK, Crump JA, et al. 2017 Infectious Diseases Society of America clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of infectious diarrhea. Clin Infect Dis. 2017 Nov 29;65(12):e45-80.
https://academic.oup.com/cid/article/65/12/e45/4557073
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29053792?tool=bestpractice.com
[24]Public Health England. Notifiable diseases and causative organisms: how to report. 26 October 2020 [internet publication].
https://www.gov.uk/guidance/notifiable-diseases-and-causative-organisms-how-to-report#list-of-notifiable-diseases
Serotyping is useful for disease surveillance and public health.[2]Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). National Shigella surveillance: Shigella annual report, 2016. 21 May 2018 [internet publication].
http://www.cdc.gov/nationalsurveillance/shigella-surveillance.html
[13]World Health Organization. Guidelines for the control of shigellosis, including epidemics due to Shigella dysenteriae type 1. 2005 [internet publication].
http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/43252/1/924159330X.pdf
Other laboratory studies and imaging
Shigellosis may cause leukocytosis, especially in more severe presentations.[5]Gastrointestinal infections and food poisoning. In: Bannister BA, Gillespie SH, Jones J. Infection: microbiology and management. 3rd ed. Oxford, UK: Blackwell Publishing Ltd.; 2006:167-201. Volume depletion may be evident with rising BUN and hematocrit. It is important that HUS is not
missed.[25]Wong CS, Jelacic S, Habeeb RL, et al. The risk of the hemolytic-uremic syndrome after antibiotic treatment of Escherichia coli O157:H7 infections. N Engl J Med. 2000 Jun 29;342(26):1930-6.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10874060?tool=bestpractice.com
Therefore, laboratory tests such as a blood smear (showing fragmentocytes) may be useful to seek this severe complication.
Abdominal x-rays may be useful if toxic dilation is suspected. In most cases, however, they are not needed, as shigellosis most often presents as a mild, self-limited illness in high-income countries. Flexible sigmoidoscopy is not usually required unless idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease is a strongly suspected differential.[26]Murphy MS. Management of bloody diarrhoea in children in primary care. BMJ. 2008 May 3;336(7651):1010-5.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2364807
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18456632?tool=bestpractice.com
