Tests
1st tests to order
indirect immunofluorescence assay (IFA)
Test
The preferred method for diagnostic confirmation because of its high sensitivity and specificity.
A definitive diagnosis should only be made with a positive serology and consistent clinical and/or paraclinical features.
There is considerable variation in cut-off titers used.[2]
Endocarditis has been diagnosed with phase I antigen IgG titer as low as 1:200 in patients with severe heart valve disease; therefore, clinical context should be carefully considered when reviewing the results.[73][79]
Result
acute infection: phase II antigen IgM titer ≥1:50 and phase II antigen IgG ≥1:200, or seroconversion; persistent focalized infection: phase I antigen IgG ≥1:800 and low or absent phase II antigen IgM
polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
Test
PCR may be used for diagnosis of acute infection before initiation of antibiotic therapy (samples should ideally be taken during the first 2 weeks of illness); however, it is not always readily available. It has the advantage of earlier diagnosis compared to serology.
PCR is highly sensitive on tissue samples such as heart valves that have higher numbers of bacteria.[74][75]
PCR can be performed on blood/serum and can yield diagnosis before seroconversion. DNA lyophilization further increases its sensitivity.[76]
Result
positive for C burnetii DNA
CBC
Test
WBC count is elevated in approximately 30% of patients. Anemia and mild thrombocytopenia (25% of cases) may be observed.[5]
Result
leukocytosis, anemia, thrombocytopenia
CRP
Test
May be elevated, particularly in cases of persistent focalized infections.
Result
elevated
LFTs
Test
In acute infection and persistent focalized infection, serum transaminases and serum alkaline phosphatase may be elevated to more than twice the normal reference range.[38] Bilirubin should be within normal ranges; however, several cases of severe hepatitis or jaundice have been reported.[2][70]
Result
elevated
activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT)
Test
Frequently prolonged in relation to the presence of a lupus anticoagulant (antiprothrombinase activity).
Highly specific for C burnetii infection in association with elevated liver enzymes.
Result
prolonged
IgG anticardiolipin (aCL) antibodies
Tests to consider
cerebrospinal fluid cell count and differential
Test
May be seen in patients with meningoencephalitis.[72]
Result
elevated WBC count with lymphocyte predominance
cerebrospinal fluid protein
Test
Patients with meningoencephalitis may show elevated protein with normal glucose.[72]
Result
elevated
cerebrospinal fluid glucose
Test
Patients with meningoencephalitis may show elevated protein with normal or low glucose.[72]
Result
normal
CXR
Test
This may be required in both acute and persistent focalized infection, if there is suspicion of pulmonary complications.
Findings may range from normal to multiple nonspecific (without apparent pattern or distribution) opacities of both lungs most consistent with an atypical pneumonia. The most common abnormalities on chest radiography are segmental or lobar opacities. The hallmark of Q fever pneumonia is a finding of several rounded opacities, but this is uncommon.[38]
Pleural effusion, atelectasis, and hilar adenopathy may also be seen, but are rare.
In the context of persistent focalized infection, CXR may identify two different persistent focalized infections: interstitial fibrosis and lung pseudotumor.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Coxiella burnetii pneumonia. CXR and CT scan from a 21-year-old woman with Coxiella burnetii pneumonia; CXR shows multiple areas of soft consolidation in the middle-to-lower lung fields bilaterally; CT scan shows poorly defined centrilobular nodules and air space consolidationOkimoto N, et al. Respirology. 2004;9:278-282; used with permission of John Wiley & Sons Ltd [Citation ends].
Result
normal or abnormal
transthoracic echocardiography (TTE)
Test
TTE is routinely recommended during acute infection to exclude underlying cardiac lesions that may be silent, and that might require antibiotic prophylaxis. In patients with acute disease and very high levels of IgG anticardiolipin (aCL) antibodies, a large transient vegetation can usually be found (acute endocarditis).[57] In patients with chronic endocarditis, vegetations are small or absent.[80] Nodular lesions and calcifications are also frequent.
Result
normal or abnormal; valvular vegetations may be seen in patients with acute disease and very high levels of IgG aCL antibodies
transesophageal echocardiography (TEE)
Test
TEE is recommended to identify cardiac lesions in patients ages >40 years who have acute infection with negative TTE and IgG anticardiolipin (aCL) antibodies ≥75 GPLU.[3]
Result
normal or abnormal; valvular vegetations may be seen in patients with acute disease and very high levels of IgG aCL antibodies
liver ultrasound
Test
This is used in acute disease if there is suspicion of liver involvement.
Findings may suggest granulomatous hepatitis.
Chronic hepatomegaly is frequently associated with endocarditis.
Result
normal or abnormal
abdominal CT scan or ultrasound
Test
Recommended in acute Q fever patients >65 years of age who smoke or have smoked in the past, or have a familial history of aneurysm. Acute Q fever in a patient with aortic aneurysm requires specific management.[3]
Result
normal or abnormal
chest CT
Test
Typically, this is not routinely required but may be used to evaluate pulmonary complications in acute disease.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Coxiella burnetii pneumonia. CXR and CT scan from a 21-year-old woman with Coxiella burnetii pneumonia; CXR shows multiple areas of soft consolidation in the middle-to-lower lung fields bilaterally; CT scan shows poorly defined centrilobular nodules and air space consolidationOkimoto N, et al. Respirology. 2004;9:278-282; used with permission of John Wiley & Sons Ltd [Citation ends].
Result
normal or abnormal
brain CT
Test
Typically, this is not routinely required but may be used to evaluate neurologic complications in acute Q fever or in endocarditis.
Result
normal or abnormal
18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET/CT imaging
Test
Critical for identifying persistent focalized infections.[78]
Is able to decipher endocarditis, vascular infection, lymphadenitis, and osteoarticular infection; these conditions cannot be identified without this technique.
It is now part of the standard anatomic check-up in patients with persistent symptoms, and/or persistent elevated serology, and/or positive polymerase chain reaction on blood/serum, or any sample with clinical presentation not consistent with primary infection.[3]
It is specifically recommended for patients: with acute Q fever with persisting phase I IgG ≥1:800 and/or sign of bad evolution; with acute Q fever with a history of vascular graft or aneurysm; or with unexplained (phase I IgG ≥1:800) serology or clinical suspicion of a persistent infection.
Also useful for identifying infection in patients with vascular prosthesis and/or aneurysm, and identifying those who require surgery with resection of infected vascular tissues. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Q fever endocarditis diagnosed at PET scan: 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose PET/CT. In this asymptomatic patient with heart valve history with elevated serology, the PET scan diagnosed an aortic endocarditis on native valve with thoracic and lumbar aortic mycotic aneurysmsInstitut Hospitalo-Universitaire Méditerranée Infection (patient consent obtained) [Citation ends].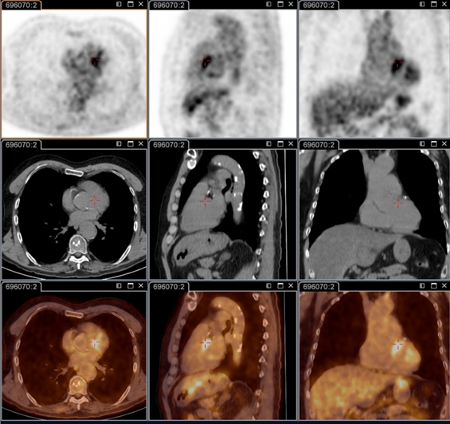 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Q fever aortic mycotic thoracic aneurysm diagnosed at PET scan: 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose PET/CT. In this asymptomatic patient with heart valve history with elevated serology, the PET scan diagnosed an aortic endocarditis on native valve with thoracic and lumbar aortic mycotic aneurysmsInstitut Hospitalo-Universitaire Méditerranée Infection (patient consent obtained) [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Q fever aortic mycotic thoracic aneurysm diagnosed at PET scan: 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose PET/CT. In this asymptomatic patient with heart valve history with elevated serology, the PET scan diagnosed an aortic endocarditis on native valve with thoracic and lumbar aortic mycotic aneurysmsInstitut Hospitalo-Universitaire Méditerranée Infection (patient consent obtained) [Citation ends].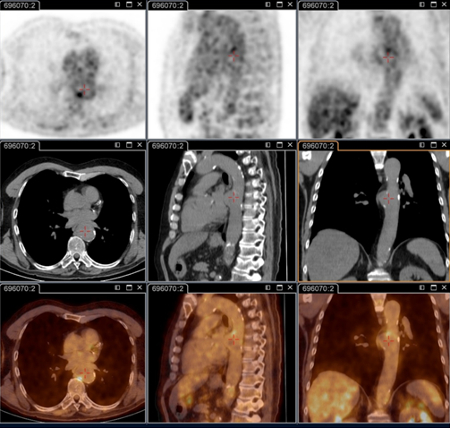 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Q fever aortic mycotic lumbar aneurysm diagnosed at PET scan: 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose PET/CT. In this asymptomatic patient with heart valve history with elevated serology, the PET scan diagnosed an aortic endocarditis on native valve with thoracic and lumbar aortic mycotic aneurysmsInstitut Hospitalo-Universitaire Méditerranée Infection (patient consent obtained) [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Q fever aortic mycotic lumbar aneurysm diagnosed at PET scan: 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose PET/CT. In this asymptomatic patient with heart valve history with elevated serology, the PET scan diagnosed an aortic endocarditis on native valve with thoracic and lumbar aortic mycotic aneurysmsInstitut Hospitalo-Universitaire Méditerranée Infection (patient consent obtained) [Citation ends].
Result
positive for persistent focalized infection (e.g., heart valve, lymphadenitis vascular focus, lymph node, osteoarticular focus)
lymph node biopsy
Test
Chronic lymphadenitis (as diagnosed by 18F-FDG PET/CT), should be routinely biopsied due to the risk of lymphoma.[64]
Result
positive for reactive lymphadenitis, granulomatous lymphadenitis, or non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphoma
immunohistochemistry
Test
Considered a gold standard test for Coxiella burnetii, but is performed only in specialist laboratories.
Immunohistochemistry has the advantage of being able to identify bacterial infection in different cell types, but is not as sensitive as fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH).[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Coxiella burnetii osteitis: immunohistochemistry: brown coloration identifies bacteria in monocytes/macrophages Hubert Lepidi, Institut Hospitalo-Universitaire Méditerranée Infection [Citation ends].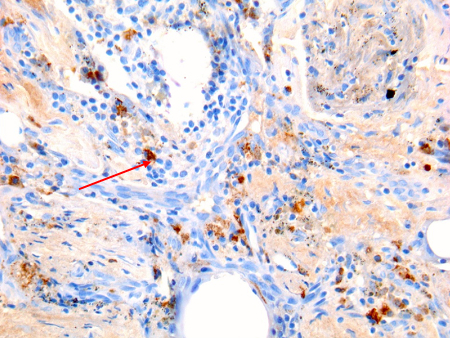 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Coxiella burnetii lung fibrosis: immunohistochemistry; brown coloration identifies bacteria in monocytes/macrophages Hubert Lepidi, Institut Hospitalo-Universitaire Méditerranée Infection [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Coxiella burnetii lung fibrosis: immunohistochemistry; brown coloration identifies bacteria in monocytes/macrophages Hubert Lepidi, Institut Hospitalo-Universitaire Méditerranée Infection [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Coxiella burnetii endocarditis: immunohistochemistry. Note the low level of inflammation. Brown coloration identifies bacteria in monocytes/macrophages inside. Vegetation is usually lackingHubert Lepidi, Institut Hospitalo-Universitaire Méditerranée Infection [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Coxiella burnetii endocarditis: immunohistochemistry. Note the low level of inflammation. Brown coloration identifies bacteria in monocytes/macrophages inside. Vegetation is usually lackingHubert Lepidi, Institut Hospitalo-Universitaire Méditerranée Infection [Citation ends].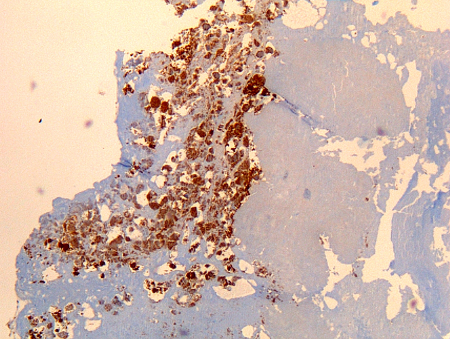 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Coxiella burnetii chronic lymphadenitis: immunohistochemistry. Note the isolated infected cell (monocytes/macrophages) in the lymph node. Brown coloration identifies bacteria in monocytes/macrophagesHubert Lepidi, Institut Hospitalo-Universitaire Méditerranée Infection [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Coxiella burnetii chronic lymphadenitis: immunohistochemistry. Note the isolated infected cell (monocytes/macrophages) in the lymph node. Brown coloration identifies bacteria in monocytes/macrophagesHubert Lepidi, Institut Hospitalo-Universitaire Méditerranée Infection [Citation ends].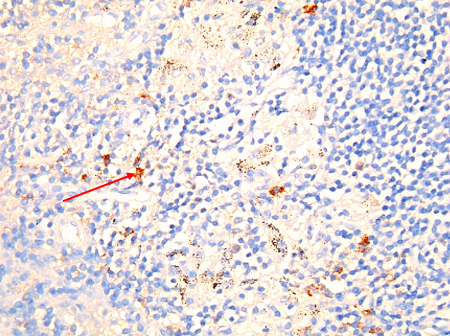 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Coxiella burnetii chronic hepatitis of a patient with endocarditis: immunohiostochemistry. Note the absence of doughnut granuloma seen in acute Q fever. Brown coloration identifies bacteria in monocytes/macrophagesHubert Lepidi, Institut Hospitalo-Universitaire Méditerranée Infection [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Coxiella burnetii chronic hepatitis of a patient with endocarditis: immunohiostochemistry. Note the absence of doughnut granuloma seen in acute Q fever. Brown coloration identifies bacteria in monocytes/macrophagesHubert Lepidi, Institut Hospitalo-Universitaire Méditerranée Infection [Citation ends].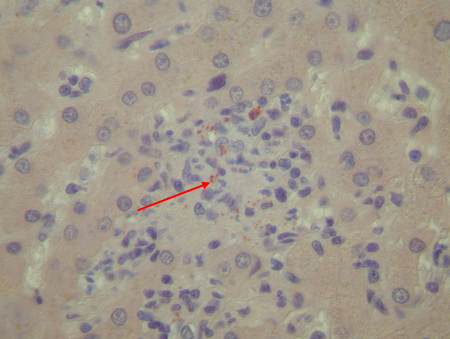
Result
positive for C burnetii bacteria
fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH)
Test
Considered a gold standard test for C burnetii, but is performed only in specialist laboratories.
FISH is more sensitive than immunohistochemistry at identifying bacterial infection in different cell types. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Coxiella burnetii lung pseudotumor: fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). Red: immunofluorescence (IF). Green: FISH with a specific 16S rRNA probe. Yellow: colocalization of IF and FISH confirms the presence of bacteria in the cytoplasm of 2 cells in a lung pseudotumor Gilles Audoly, Institut Hospitalo-Universitaire Méditerranée Infection [Citation ends].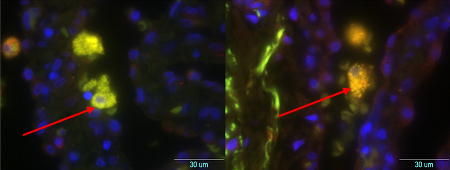
Result
positive for C burnetii bacteria
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer