Tests
1st tests to order
spirometry
Test
Spirometry should be performed in all patients with suspected occupational asthma.[22][71] If spirometry is not available, peak expiratory flow (PEF) may be used.[57] PEF is less objective than spirometry.
Excessive variability in expiratory lung function is suggestive of a diagnosis of asthma.[57]
A bronchodilator reversibility test should be performed in patients presenting with work-related respiratory symptoms. An increase in forced expiratory volume at 1 second (FEV1) and/or forced vital capacity (FVC) of >12% and >200 mL from baseline following a bronchodilator has been considered to be a significant change.[57] Guidance from the American Thoracic Society (ATS) and European Respiratory Society (ERS) suggests that an increase in FEV1 of >10% of predicted following a bronchodilator is considered a significant response.[76]
Result
FEV1/FVC <80% of predicted; increase in FEV1 and/or FVC of >12% and >200 mL from baseline following a bronchodilator; increase in FEV1 >10% of predicted following a bronchodilator
chest x-ray
Test
Not diagnostic of asthma.
Indicated in the assessment of respiratory symptoms to exclude other pathologies.[62]
Result
normal or hyperinflated; exclude signs of infection in acute exacerbation
skin prick testing (SPT)
Test
A positive reaction may be defined as a wheal ≥3 mm diameter, or a diameter that is greater than or equal to that of the histamine control. Generally reactions are assessed at 10-15 minutes. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Skin prick test results with natural rubber latex in a nurse with occupational asthmaFrom Tarlo SM, Wong L, Roos J, et al. Occupational asthma caused by latex in a surgical glove manufacturing plant. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1990:85:626-631. Used with permission [Citation ends].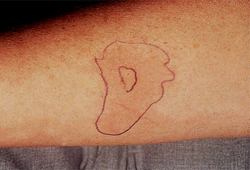
An immediate wheal and flare (IgE-mediated) in response to common environmental allergens such as pollens and dust mites indicates the presence of atopy.
Reports on the sensitivity and specificity of SPT vary, but the results of one meta-analysis suggest a pooled sensitivity and specificity of 80.6% and 59.6%, respectively, for high molecular weight agents compared with specific inhalation challenge.[66]
SPT should be used in combination with a clinical history and supportive pulmonary function tests.[22][36][52][66][68][71]
There are few commercially available or standardized skin reagents for occupational agents.
Result
positive for allergen
nonspecific bronchial hyper-responsiveness (NSBHR)
Test
A positive challenge test (methacholine or histamine) supports the diagnosis of asthma for any patient with suspected sensitizer-induced or irritant-induced occupational asthma (OA). A PC20 ≤8 mg/mL is usually taken as supportive of asthma.[36][66][68] A PC20 that increases more than 3-fold (indicating less bronchial hyper-responsiveness) is significant, and a 2-fold increase is of possible significance.[1][61][77]
A challenge that significantly improves when the patient is away from work supports the diagnosis of sensitizer-induced OA, unless confounding factors such as a respiratory tract infection are present.[22][36][66][68][71]
Serial tests (at work and off work) should be performed within 8 weeks. The off-work test should be performed after at least 10 days away from work.[36][66][68]
Diagnosis of irritant-induced OA is supported by progressive improvement in methacholine or histamine responsiveness after an initial positive response following the exposure incident. However, absence of improvement does not exclude the diagnosis.[36][66][68]
Result
provocative concentration causing a 20% fall in forced expiratory volume at 1 second (FEV1; PC20) ≤8 mg/mL; improvement in PC20 when away from work exposure
serial peak expiratory flow (PEF)
Test
Serial PEF recordings are useful when the patient is still exposed to the potential causal agent and is able to record measurements during and away from work.[22][71]
Recordings should made in triplicate at least 4 times a day (before work, mid shift, end of shift, and bedtime, with similar recording off work) for ≥3 weeks with concurrent recording of symptoms, exposures, and drugs.[22]
Results may be interpreted by visual inspection of graphs or by computerized programs.
Plotting of results and visual inspection relative to work exposures can provide an indication as to whether there are functional airway changes in relation to work.[36][69][72][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Peak expiratory flow (PEF) and results of methacholine challenge in a patient with occupational asthmaFrom Tarlo SM, Wong L, Roos J, et al. Occupational asthma caused by latex in a surgical glove manufacturing plant. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1990:85:626-631. Used with permission [Citation ends].
Result
work-related increase in diurnal variability of PEF
Tests to consider
specific serum IgE assay
Test
Specific serum IgE to low molecular weight sensitizers such as diisocyanates, trimellitic anhydride, and platinum salts may be demonstrated in some patients with sensitizer-induced occupational asthma.[22][36][53][71][78]
Specific serum IgE antibodies to high molecular weight allergens may be demonstrated, adding to diagnostic certainty. IgE antibodies to sensitizers may, however, be demonstrated in a proportion of asymptomatic exposed workers.[36][38]
For many occupational allergens, serum IgE antibodies are less sensitive but more specific for the diagnosis than skin prick testing.[79]
Performed only in specialized laboratories and used primarily for research purposes.[36][66][68]
Result
positive
specific inhalation challenge (SIC)
Test
SIC is considered to be the reference standard diagnostic investigation for sensitizer-induced occupational asthma.[22][36][52][67][71] However, it may only be available in a few specialized centers.
Challenges are performed in a controlled exposure facility with the suspected workplace sensitizer, preferably with a placebo exposure in a single-blinded manner. Spirometry is recorded before and at periods after exposure (for several hours) to detect a significant change from baseline. Nonspecific bronchial hyper-responsiveness (NSBHR) and (if available) induced sputum cytology are assessed at baseline and postexposure. Challenges can be false-positive and false-negative, but the frequency of these false results is unknown.
A reproducible fall of 15% to 20% in forced expiratory volume at 1 second (FEV1) from the prechallenge value generally signifies a "positive" test.
NSBHR and/or sputum eosinophils may also increase in a positive response.[80]
Result
positive (reproducible fall of 15% to 20% in FEV1 from the prechallenge value)
Emerging tests
induced sputum cytology
Test
Increased sputum eosinophil count has been demonstrated with exposure to a sensitizer at work and associated with specific challenges. Sputum cytology is a potentially useful addition to the diagnostic panel of tests for sensitizer-induced occupational asthma.[36][42]
May increase the sensitivity of specific inhalation challenge (SIC).[22]
Has a high sensitivity and specificity for the diagnosis of asthma when combined with fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO).[81]
Result
increased sputum eosinophil count; may improve away from workplace
fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO)
Test
The role of FeNO in the routine diagnosis of occupational asthma is not yet established.[22][36][82][83]
May increase the sensitivity of specific inhalation challenge (SIC).[22]
Has a high sensitivity and specificity for the diagnosis of asthma when combined with induced sputum cytology.[81]
Result
variable; may be increased
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer