Differentials
Community-acquired pneumonia
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Acute pulmonary blastomycosis is commonly mistaken for community-acquired pneumonia. Failure to respond to antibacterial therapy and extrapulmonary manifestations are clues to the etiology.[30]
INVESTIGATIONS
Findings of blastomycosis on chest radiograph can be atypical for community-acquired pneumonia, and include mass-like or cavitary lesions or diffuse interstitial infiltrates. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Pulmonary blastomycosis with focal infiltrates on chest radiographDr Robert Orenstein, DO, Associate Professor of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases, Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, AZ [Citation ends].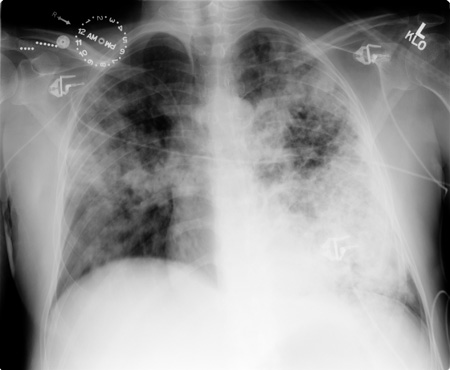 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Pulmonary blastomycosis presenting as a miliary pattern on chest radiographDr Robert Orenstein, DO, Associate Professor of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases, Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, AZ [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Pulmonary blastomycosis presenting as a miliary pattern on chest radiographDr Robert Orenstein, DO, Associate Professor of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases, Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, AZ [Citation ends].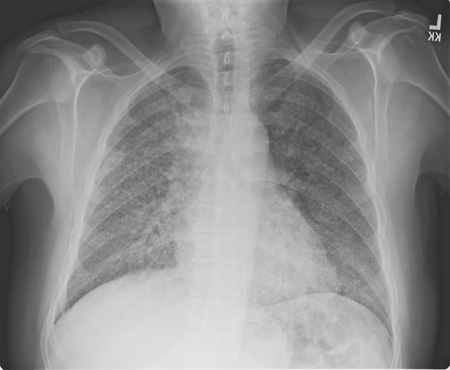 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Close up of reticulonodular findings on chest radiography in disseminated blastomycosisPersonal files of Larry Baddour, MD [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Close up of reticulonodular findings on chest radiography in disseminated blastomycosisPersonal files of Larry Baddour, MD [Citation ends].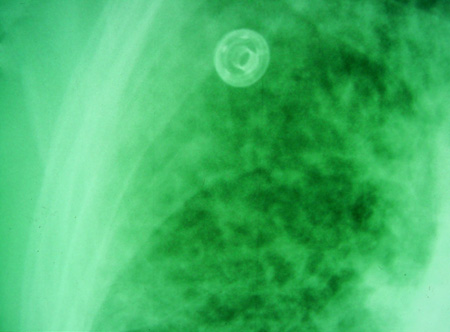
A positive Blastomyces dermatitidis enzyme immunoassay (EIA) urine antigen test indicates probable acute pulmonary blastomycosis, though this may not be available in some centers.[30][31]
Histoplasmosis
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Histoplasmosis and blastomycosis share many of the same clinical manifestations, and the endemic areas overlap to a great extent.
However, sputum in blastomycosis is generally purulent, in contrast to histoplasmosis.
INVESTIGATIONS
Differentiation between these 2 diseases often relies on culture data. Histoplasma yeast are typically smaller, have narrow-based budding, and are found intracellularly within macrophages in clinical specimens. There is some cross reactivity with serologic and antigen assays for these 2 organisms.
Coccidioidomycosis
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Coccidioidomycosis and blastomycosis share many of the same clinical manifestations. However, the endemic area of Coccidioides is the desert region of the southwestern US.
INVESTIGATIONS
Serologic testing for coccidioidomycosis is of higher sensitivity than for blastomycosis, and the yeast in pathologic specimens appears as the characteristic spherule.
Paracoccidioidomycosis
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Acute/subacute paracoccidioidomycosis more often presents with lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, and bone marrow dysfunction, while chronic paracoccidioidomycosis generally presents with dry cough and dyspnea.
Paracoccidioidomycosis is also endemic to Central and South America.
INVESTIGATIONS
Paracoccidioides yeast are typically smaller than Blastomyces dermatitidis with thinner cell walls, and can be found in the mariner wheel formation, with multiple small budding yeast circumferentially surrounding the parent cell.[35]
Sporotrichosis
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
The cutaneous lesions of sporotrichosis are similar in appearance to blastomycosis. However, lymphadenitis (generally nodular, and subacute to chronic) is pathognomonic in sporotrichosis.
INVESTIGATIONS
Microbiologic and pathologic examination of skin biopsies will yield the diagnosis.
Tuberculosis
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Cutaneous disease is less common in tuberculosis than in blastomycosis.
INVESTIGATIONS
Acid fast smear and mycobacterial culture of clinical specimens generally lead to the diagnosis of tuberculosis. Tuberculin skin testing and the in vitro interferon gamma release assays of sensitized lymphocytes are also helpful in diagnosis of tuberculosis.
Nocardiosis
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Nocardiosis and blastomycosis share many of the same clinical features. Nocardia is more common in people who are immunocompromised and has a worldwide distribution.
INVESTIGATIONS
Microbiological examination of clinical specimens in nocardiosis reveals thin, branching gram-positive bacilli that stain positively by the modified acid fast stain. Culture of Nocardia species is confirmatory of that diagnosis.
Malignancy
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
The pulmonary, cutaneous, osteoarticular, and central nervous system manifestations of blastomycosis can all be mistaken for primary or metastatic neoplasms.
INVESTIGATIONS
Pathologic examination of tissue specimens can confirm or rule out malignancy.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer