History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
common
visualization of cerumen
Varies in consistency from soft to hard and in color from yellow to brown or black. It can also appear more dry, yellow, and flaky in Asian people compared to non-Asian people.[3][4] It may be present in the lateral part of the ear canal alone, or may fill the entire canal. It may be impacted onto the tympanic membrane, particularly if there was use of a cotton-tipped applicator. A "veil" of cerumen is sometimes seen. Visualization can be done using an otoscope, a handheld speculum, or a binocular microscope.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: The colors of cerumenReprinted with permission from: Hawke M. Ear disease: a clinical guide. Hamilton, London: Decker DTC, 2003 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Dry, flaky cerumen seen in Asian peopleReprinted with permission from: Hawke M. Ear disease: a clinical guide. Hamilton, London: Decker DTC, 2003 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Dry, flaky cerumen seen in Asian peopleReprinted with permission from: Hawke M. Ear disease: a clinical guide. Hamilton, London: Decker DTC, 2003 [Citation ends].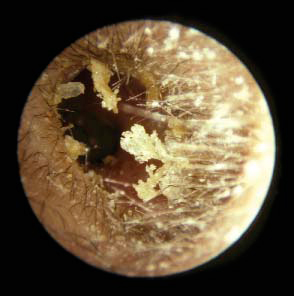 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Veil of cerumenReprinted with permission from: Hawke M. Ear disease: a clinical guide. Hamilton, London: Decker DTC, 2003 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Veil of cerumenReprinted with permission from: Hawke M. Ear disease: a clinical guide. Hamilton, London: Decker DTC, 2003 [Citation ends].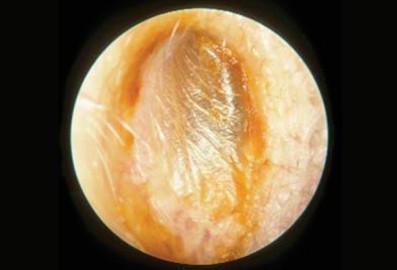
hearing loss
Onset of hearing loss in the involved ear over the last few days, weeks, or months.
Findings that are characteristic are a conductive hearing loss, or a mixed hearing loss where the conductive component due to the impaction is superimposed on the underlying sensorineural hearing loss.
fullness in the ear
Feeling of occlusion of the involved ear, usually occurring in conjunction with hearing loss.
Other diagnostic factors
common
uncommon
otalgia
Does not occur usually with uncomplicated cerumen impaction. It may be a symptom of otitis externa.
tinnitus
Also occurs with other causes of hearing loss but is a rarer symptom of cerumen impaction.
cough
May occur from stimulation of ear-canal skin.
vertigo
Can be a symptom but rarely due to cerumen impaction. May occur when the ear wax pushes against the tympanic membrane.
Risk factors
strong
age >50 or <5 years
male sex
Older men tend to have more hair in their ear canals. The exfoliated hair becomes incorporated in the cerumen, making the cerumen harder and more difficult to extrude naturally from the ear canal.
stenotic ear canal
Anatomically, it does not take as much cerumen to occlude a small ear canal than to occlude a larger canal. Individuals with stenotic external auditory canals tend to have a proclivity for cerumen impactions.[4]
Down syndrome
Up to 40-50% of newborns with Down syndrome (trisomy 21) have stenotic ear canals, predisposing them to cerumen impactions.[7] Additionally, the presence of a cognitive impairment might limit an individual's awareness of the impaction and/or their ability to complain of the symptoms caused by the impaction.
cotton-tipped applicator use
People who use cotton-tipped applicators in their own ears tend to push the cerumen medially toward the tympanic membrane, often causing cerumen impaction. Whether the cotton-tipped applicators are used for drying the ear canal, for relief of pruritus, or to attempt cerumen removal, the end result is often impaction of cerumen deeper into the ear canal. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Impacted cerumen caused by instrumentation of the ear canal with a cotton-tipped applicatorReprinted with permission from: Hawke M. Ear disease: a clinical guide. Hamilton, London: Decker DTC, 2003 [Citation ends].
weak
hearing aid use
The action of inserting a hearing aid may result in impaction of previously unimpacted cerumen.
living in a nursing home
In one study, residents of nursing homes exhibited a 40% prevalence of impacted cerumen.[8] An individual with a cognitive impairment might not be aware of the presence of the cerumen impaction and/or might not be able to complain of the symptoms caused by the impaction.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer