Investigations
1st investigations to order
retinoscopy
Test
Retinoscopy is the most practical office procedure to determine an objective refraction.
The fundamental components of a retinoscope are a light source, a condensing lens, a mirror, and a sleeve. The clinician projects the light streak towards the patient's eye (usually in a working distance of 66 cm), and a red reflex from the retina passes back to the clinician's eye. By observing and analysing the properties of the reflex, the examiner can determine the refractive state of the patient.
The clinician should sweep the light streak from side to side and observe the direction of the red reflex, which can be with the motion of the sweep or against it. In general terms, when a 'with' motion is seen, a plus lens of gradually increasing power should be placed in front of the eye until no motion is seen (neutralisation). When an 'against' motion is observed, a minus lens of gradually increasing power should be placed in front of the eye until neutralisation is achieved.
When neutralisation is obtained in all meridians using the same dioptric power lens, the eye is said to have a spherical refractive error (myopia or hyperopia). However, when different dioptric power is needed to reach neutralisation in different meridians, astigmatism is diagnosed. This difference in the dioptric power is the power of astigmatism and the principal meridians are localised to determine the axis.[29]
Result
any irregularity in the width of the retinal reflex while rotating the light streak of the retinoscope 5 cm in front of the patient's eye indicates astigmatism
Investigations to consider
keratometry
Test
The keratometer is a reflection-based method of detecting astigmatism. Light is projected onto the cornea, which acts like a convex mirror to produce a virtual upright image. The ratio of the image and object diameters is used to estimate the radius of curvature along a particular meridian.
A keratometer determines the corneal curvature only in the steepest meridian and on the meridian 90° away. For that reason, the instrument is very accurate for a regular spherocylindrical cornea, but it is of less value in irregular astigmatism. Furthermore, the keratometer is less accurate for corneal powers <36 or >50 dioptres.[40]
Result
astigmatism is present when a significantly different corneal power is measured in the principal meridians
corneal topography
Test
In this technique, computerised instruments gather raw data about the dimensions and curvature of the cornea. Using these data, coloured maps of the cornea with warm colours (reds and oranges) representing steep curvatures of the cornea and cooler colours (blues) representing less steep curvatures can be produced. The software can manipulate and display the raw data in many ways and can delineate the major and minor axes of the cornea. It is also useful for planning refractive surgery and evaluating post-operative results.[41]
Corneal topography can diagnose and monitor corneal pathologies, including irregular astigmatism, corneal warpage, or signs of keratoconus or other corneal ectasias that may be associated with unpredictable outcomes.[42]
Scheimpflug device may be considered when posterior corneal curvature measurement is important (e.g., in post-operative astigmatism following cataract surgery).[39][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Corneal topography: with-the-rule astigmatismFrom the collection of the Department of Ophthalmology, Assaf Harofeh Medical Center, Israel. Used with permission [Citation ends].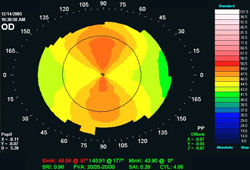 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Corneal topography: against-the-rule astigmatismFrom the collection of the Department of Ophthalmology, Assaf Harofeh Medical Center, Israel. Used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Corneal topography: against-the-rule astigmatismFrom the collection of the Department of Ophthalmology, Assaf Harofeh Medical Center, Israel. Used with permission [Citation ends].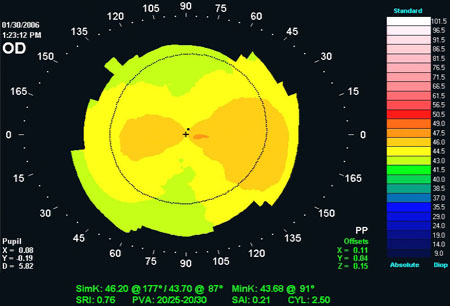 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Corneal topography: oblique astigmatismFrom the collection of the Department of Ophthalmology, Assaf Harofeh Medical Center, Israel. Used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Corneal topography: oblique astigmatismFrom the collection of the Department of Ophthalmology, Assaf Harofeh Medical Center, Israel. Used with permission [Citation ends].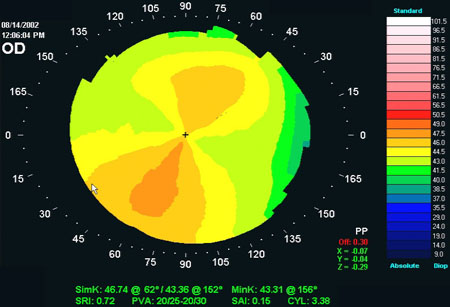 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Corneal topography: keratoconusFrom the collection of the Department of Ophthalmology, Assaf Harofeh Medical Center, Israel. Used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Corneal topography: keratoconusFrom the collection of the Department of Ophthalmology, Assaf Harofeh Medical Center, Israel. Used with permission [Citation ends].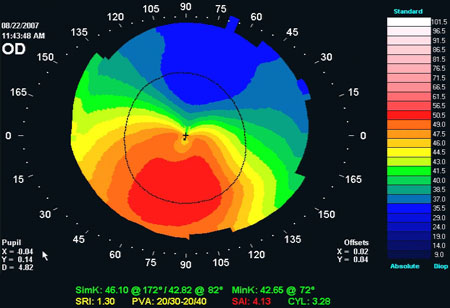
Result
different corneal power in different meridians establishes the diagnosis of astigmatism
wavefront analysis technology
Test
An aberration map of the eye is created by comparing the shape of the captured wavefront with that of the pre-programmed reference wavefront, measuring all points of difference between the two, creating a wavefront map of the examined eye.
Result
astigmatism, if present, will be graphically presented on the aberration map
anterior-segment optical coherence tomography (AS-OCT)
Test
A non-contact imaging system that uses optical light reflection to produce high-resolution, cross-sectional images of the cornea. It may be considered when posterior corneal curvature measurement is important (e.g., in post-operative astigmatism following cataract surgery).[39]
Result
different corneal power in different meridians establishes the diagnosis of astigmatism
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer