Last reviewed: 16 Mar 2025
Last updated: 28 Jan 2025
Summary
Definition
History and exam
Other diagnostic factors
- heartburn
- regurgitation
- obesity
- chest pain
- dysphagia
- odynophagia
- haematemesis
- shortness of breath
- cough
- oropharyngitis
- wheezing
- non-bilious vomiting
- fever and chills
- confusion
Risk factors
- obesity
- increased age
- previous gastro-oesophageal procedure
- elevated intra-abdominal pressure
- male sex
- incisional, umbilical, or inguinal hernia
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
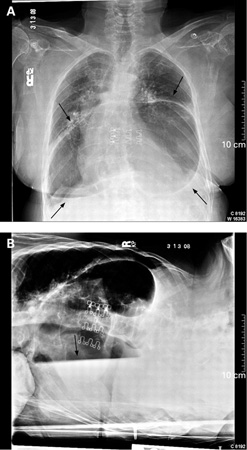
- chest x-ray
- upper gastrointestinal fluoroscopy with oral contrast
Investigations to consider
- oesophago-gastro-duodenoscopy
- CT scan or MRI scan
- high-resolution oesophageal manometry and pH monitoring
Treatment algorithm
Contributors
Authors
Constantine T. Frantzides, MD, PhD, FACS

Director
Chicago Institute of Minimally Invasive Surgery
St. Francis Hospital
Clinical Professor of Surgery
University of Illinois Chicago
Chicago
IL
Disclosures
CTF declares that he has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Constantine T. Frantzides would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Mark A. Carlson, Dr Amy J. Hargrove and Dr Minh B. Luu, previous contributors to this topic.
Disclosures
MAC, AJH and MBL declare they have no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Frank A. Granderath, MD
Associate Professor
Department of General, Visceral and Transplant Surgery
University Hospital Tuebingen
Germany
Disclosures
FAG declares that he has no competing interests.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer