History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
common
presence of risk factors
Key risk factors include: exposure to varicella, young age, immunisation status, and occupation.
fever
Usually <38°C (101.5°F), but may be as high as 41°C (106°F).[6]
Secondary bacterial infection should be considered in patients with persistent (i.e., >3 days) or recurrent fever.
vesicular rash
Classically described as a dew drop on a rose petal. The rash usually first appears centrally (on the face, scalp, or torso), before spreading to the extremities.[62]
Lesions first appear as macules and quickly develop into fluid-filled vesicles.
As the disease progresses, early lesions will begin to scab over as new peripheral lesions develop. This appearance of lesions in 'crops' (i.e., different stages of acuity/healing) is characteristic of varicella.
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Typical vesicular rash of primary varicella; note that lesions are in different stagesImage provided by the CDC and the Public Health Image Library [Citation ends].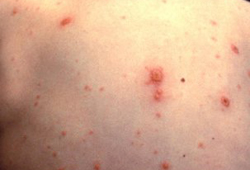 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Varicella lesions in different stages of healingImage provided by the CDC [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Varicella lesions in different stages of healingImage provided by the CDC [Citation ends].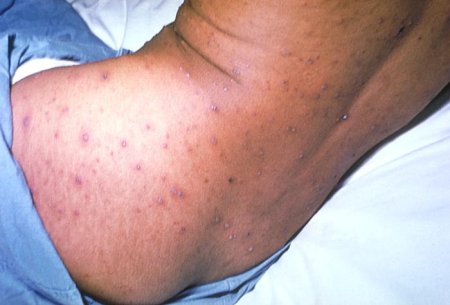
vesicles on mucous membranes
Found most commonly in nasopharynx, but also on other mucous membranes such as conjunctiva, mouth, and vulva. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Varicella lesion on the hard palate of a young patientImage provided by the CDC and the Public Health Image Library [Citation ends].
Other diagnostic factors
common
pruritus
May be a feature in some patients prior to the onset of the rash.
headache
May be a feature in some patients prior to the onset of the rash.
fatigue/malaise
May be a feature in some patients prior to the onset of the rash.
sore throat
May be a feature in some patients prior to the onset of the rash.
tachycardia
May be present in infected patients.
Risk factors
strong
exposure to varicella
Occurs through family contacts or day care- or school-related exposure.
age 1 to 9 years
Most common at-risk group is children aged 1 to 9.
unimmunised status
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer