Criteria
No diagnostic criteria
There are no diagnostic criteria, but the classification criteria below are helpful if systemic sclerosis is suspected. However, in early disease, the clinical features may not reach the threshold for classification of systemic sclerosis even if a clinical diagnosis of systemic sclerosis has been made.
Clinical classification: scleroderma
Non-systemic
Systemic
Limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis
Diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis
Systemic sclerosis sine scleroderma
Indeterminate subset
Overlap syndromes with other connective tissue diseases
2013 classification criteria for systemic sclerosis: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative[27]
These criteria are applicable to any patient considered for inclusion in a systemic sclerosis study. The criteria are not applicable to patients with skin thickening sparing the fingers or to patients who have a scleroderma-like disorder that better explains their manifestations (e.g., nephrogenic sclerosing fibrosis, generalised morphea, eosinophilic fasciitis, scleroedema diabeticorum, scleromyxoedema, erythromyalgia, porphyria, lichen sclerosis, graft-versus-host disease, diabetic cheiroarthropathy). The total score is determined by adding the maximum weight (score) in each category.
Patients with a total score of ≥9 using the following criteria are classified as having definite systemic sclerosis:
Skin thickening of the fingers (only count the highest score out of the following 3 items)
Both hands extending proximal to the metacarpophalangeal joints (9 points)
Puffy fingers (2 points)
Sclerodactyly of the fingers distal to the metacarpophalangeal joints but proximal to the proximal interphalangeal joints (4 points)
Fingertip lesions (only count the higher score out of the following 2 items)
Digital tip ulcers (2 points)
Fingertip-pitting scars (3 points)
Telangiectasia (2 points)
Abnormal nailfold capillaries (2 points)
Pulmonary arterial hypertension and/or interstitial lung disease (maximum score of 2)
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (2 points)
Interstitial lung disease (2 points)
Raynaud's phenomenon (3 points)
Systemic sclerosis-related auto-antibodies such as anti-centromere, anti-topoisomerase I (anti-Scl 70), and anti-RNA polymerase III (3 points).
Limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis and diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis[1]
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Characteristics of limited scleroderma versus diffuse sclerodermaAdapted from LeRoy EC, Black C, Fleischmajer R, et al. Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis): classification, subsets and pathogenesis. J Rheumatol. 1988;15:202-205. [Citation ends].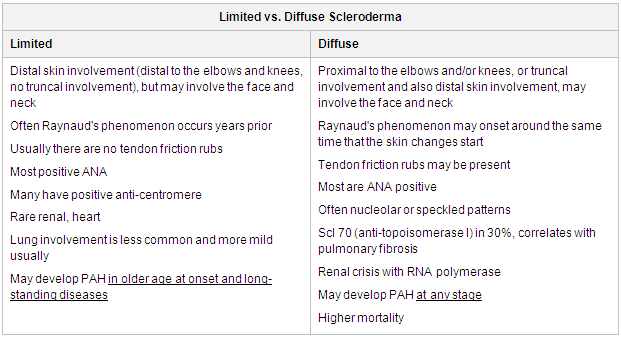
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer