Investigations
1st investigations to order
CT and/or MRI head scan
Test
May show meningeal involvement and enhancement, parenchymal lesions, hydrocephalus.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Cryptococcal meningoencephalitis. (A) Cranial magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) shows cerebellar hyperintensities (arrows) in FLAIR sequences (fluid-attenuated inversion recovery) and (B) meningeal contrast enhancement (arrows) in T1 weighted MRI. (C) Indian ink stain, (D) fungal culture, and (E) Gram stain of cerebrospinal fluid were positiveBraun J. Headache, personality changes and fine motor disturbances. BMJ Case Reports. 2009; doi:10.1136/bcr.06.2008.0093. Used with permission. [Citation ends].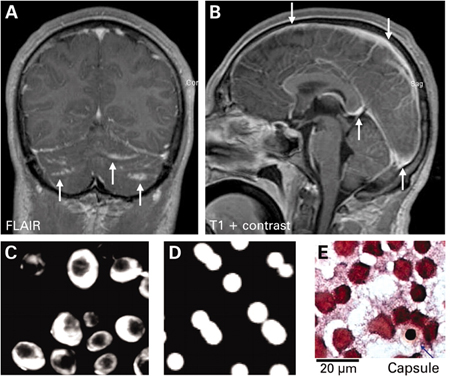
A normal scan does not rule out fungal meningitis.
Result
normal or demonstrating enhancement, parenchymal lesions, hydrocephalus
fungal blood cultures (3 sets)
Test
Up to three sets of fungal blood tests should be taken.
May be positive when candidal, histoplasmal, or cryptococcal meningitis is associated with disseminated disease.
Result
positive or negative
serum cryptococcal antigen test
Test
Recommended in all immunocompromised patients with undiagnosed or suspected fungal meningitis.
High sensitivity and specificity for HIV-associated cryptococcal disease.
Useful if cerebrospinal fluid cannot be obtained.
Result
positive in cases of cryptococcal meningitis
serum + urine Histoplasma antigen
Test
Recommended in all immunocompromised patients with undiagnosed or suspected fungal meningitis who live in or have visited the endemic area.
Sensitivity for diagnosing histoplasmal meningitis is around 70% and 40% for urine and serum, respectively.[27]
Very specific.
Result
positive in majority of cases of progressive disseminated histoplasmosis
immunodiffusion tests (IgM and IgG) and complement fixation test (IgG) for coccidioidomycosis
Test
Recommended in all immunocompromised patients with undiagnosed or suspected fungal meningitis who live in or have visited the endemic area.
Positive results support the diagnosis of coccidioidal meningitis when other causes of meningitis are excluded. Negative results from an experienced laboratory in patients with untreated disseminated disease are rare.[11]
Result
typically positive in cases of coccidioidal meningitis
cerebrospinal fluid opening pressure
Test
Very high opening pressure suggestive of HIV-associated cryptococcal meningitis in the appropriate context.
Result
elevated
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) WBC and differential
Test
Most cases of fungal meningitis have a lymphocytic pleocytosis in the range of 20 to 500 cells/microlitre.
A predominance of polymorphonuclear cells may occur and is suggestive of meningitis due to Candida and opportunistic mould infections (Aspergillus, Zygomycetes, Pseudallescheria).
CSF eosinophils are uncommon, but suggestive of coccidioidal meningitis in the appropriate context.
Normal CSF white cell counts are common in HIV-associated cryptococcal meningitis.
Result
elevated
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) protein
Test
In fungal meningitis, CSF protein is typically elevated.
Result
elevated
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) glucose
Test
In fungal meningitis, CSF glucose is typically low.
Result
low
cerebrospinal fluid India ink stain
Test
Recommended in all immunocompromised patients with chronic or subacute, undiagnosed or suspected fungal meningitis.
Sensitivity is approximately 80% in HIV-associated cryptococcal meningitis.[58]
Less sensitive in non-HIV-associated cryptococcal meningitis.
Result
positive in cryptococcal meningitis
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) culture
Test
To increase sensitivity, large volumes of CSF (≥10 mL) and prolonged incubation (at least 2 weeks) may be needed.
Repeat if initially negative, or initially low volume.
Result
positive or negative
cerebrospinal fluid cryptococcal polysaccharide antigen test
Test
Recommended in all immunocompromised patients with chronic or subacute, undiagnosed or suspected fungal meningitis.
Sensitivity higher than India ink.
Very specific at a titre ≥1:8; high titres indicate poor prognosis.
Result
positive in cryptococcal meningitis
cerebrospinal fluid Histoplasma antigen
Test
Recommended in all immunocompromised patients with chronic or subacute, undiagnosed or suspected fungal meningitis who live in or have visited the endemic area.
Sensitivity around 70% and 40%, in HIV- and non-HIV-associated cases, respectively.[27]
Very specific.
Result
positive in histoplasmal meningitis
cerebrospinal fluid Histoplasma antibodies
Test
Recommended in all immunocompromised patients with undiagnosed or suspected fungal meningitis who live in or have visited the endemic area.
Sensitivity and specificity around 80%.[27]
Result
positive in histoplasmal meningitis
cerebrospinal fluid coccidioidal IgG antibodies
Test
Recommended in all immunocompromised patients with undiagnosed or suspected fungal meningitis who live in or have visited the endemic area.
Provides specific diagnosis in coccidioidal meningitis.
Result
positive in coccidioidal meningitis
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) galactomannan antigen test
Test
Galactomannan detection in CSF showed a good diagnostic performance when an optical density index cutoff of 0.5 to 2.0 was used.[85]
Result
positive in Aspergillus meningitis
Investigations to consider
histopathology and culture of biopsies: meningeal, brain, extraneural sites of involvement
Test
Considered if less invasive tests are negative.
Result
positive for organism
Emerging tests
18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET/CT
Test
FDG PET/CT scanning identifies tissue with an enhanced glucose metabolism. Apart from the evaluation of malignancies, FDG PET/CT has been used in the diagnosis of focal inflammation and infection.
In one study, FDG PET/CT informed therapy duration decisions, and highlighted the need for surgery, in lymphoid/myeloid malignancy patients with complex invasive fungal disease.[84]
Result
detection of tissue with enhanced glucose metabolism, such as focus of fungal infection
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) (1-3)-beta-D-glucan
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer