Investigations
1st investigations to order
transthoracic or transoesophageal echocardiogram
Test
Performed at time of general assessment of TR.
Particular attention should be given to right ventricle function/dilation, valve morphology/function, and tricuspid valve annular size, factors that determine valve repair versus replacement. Pulmonary artery pressure should also be assessed. A transoesophageal echocardiogram can be performed if the transthoracic approach does not yield adequate quality images for accurate assessment.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Severe tricuspid regurgitation due to annular enlargement. A. Systolic frame from apical 4 chamber view (Mayo Clinic display format with right ventricle on the right). Note tricuspid annular enlargement measuring 4.2 cm and tethering of the tricuspid leaflets leading to failure of coaptation of the tricuspid valve. B. Massive tricuspid regurgitation on Colour Doppler. C. Continuous Wave Doppler through the tricuspid valve. Note the dagger-shaped tricuspid regurgitant signal (arrows), consistent with rapid equalisation of pressures between right ventricle and right atrium, typical of massive tricuspid regurgitation. D. Pulsed Wave Doppler of the hepatic veins demonstrates late systolic flow reversals consistent with severe tricuspid regurgitation.From the collection of Sorin V. Pislaru, Mayo Clinic [Citation ends].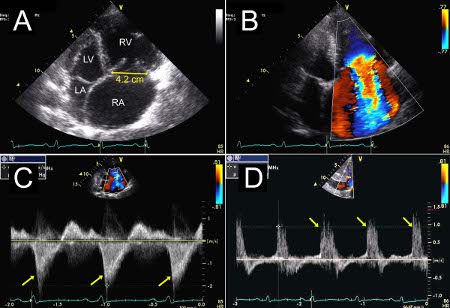
Result
assessment of left and right heart ejection fraction/dilation, valve morphology/function; evidence of pericardial disease, constrictive/restrictive physiology, may show regional wall motion abnormalities
ECG
Test
Performed at time of general assessment of TR and as part of preoperative assessment.
Result
may show atrial flutter/fibrillation; presence of previous myocardial infarction
LFTs
Test
Patients with chronic severe TR often develop ascites from advanced liver disease, from chronic congestion or fibrosis (cardiac cirrhosis).
Result
normal or abnormal
serum urea and creatinine
Test
Related to renal abnormality.
Result
normal or elevated
FBC
Test
Related to renal and liver abnormality.
Result
anaemia (e.g., anaemia of chronic disease, renal failure), thrombocytopenia (e.g., due to liver failure and cirrhosis)
CXR
Test
Assesses for heart failure/enlargement.
Result
may show cardiomegaly, pleural or pericardial effusion, presence of pacemaker
Investigations to consider
operative transoesophageal echocardiogram
Test
Particular attention should be given to right ventricle function/dilation, valve morphology/function, and tricuspid valve annular size - factors that determine valve repair versus replacement. Pulmonary artery pressure should be assessed.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Severe tricuspid regurgitation due to carcinoid valvular disease. A. Systolic frame from mid-oesophageal 4 chamber view. Note thickened tricuspid leaflets, but also retracted and thickened chordae, typical of advanced carcinoid valvular disease (arrows). The right ventricle and right atrium are enlarged. The atrial septum is deviated to the left, demonstrating right atrial pressure is higher than left atrial pressure (asterisk). B. Colour Doppler demonstrating severe tricuspid regurgitation. Vena contracta measured 1.2 cm, consistent with the coaptation gap on 2D images and virtually free flow between the right ventricle and right atrium.From the collection of Sorin V. Pislaru, Mayo Clinic [Citation ends].
Result
assessment of left and right heart ejection fraction/dilation and valve morphology/function, may show regional wall motion abnormalities
postoperative transthoracic echocardiogram
Test
Particular attention should be given to right ventricle function/dilation, valve morphology/function, and tricuspid valve annular size, factors that determine valve repair versus replacement. Pulmonary artery pressure should also be assessed.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Severe tricuspid regurgitation due to annular enlargement. A. Systolic frame from apical 4 chamber view (Mayo Clinic display format with right ventricle on the right). Note tricuspid annular enlargement measuring 4.2 cm and tethering of the tricuspid leaflets leading to failure of coaptation of the tricuspid valve. B. Massive tricuspid regurgitation on Colour Doppler. C. Continuous Wave Doppler through the tricuspid valve. Note the dagger-shaped tricuspid regurgitant signal (arrows), consistent with rapid equalisation of pressures between right ventricle and right atrium, typical of massive tricuspid regurgitation. D. Pulsed Wave Doppler of the hepatic veins demonstrates late systolic flow reversals consistent with severe tricuspid regurgitation.From the collection of Sorin V. Pislaru, Mayo Clinic [Citation ends].
Result
assessment of left and right heart ejection fraction/dilation and valve morphology/function, may show regional wall motion abnormalities
cardiac catheterisation
Test
Elevated pulmonary artery pressure is an important factor for choosing valve repair over replacement. In addition, right ventricular function is an important variable in pre-operative risk stratification. However, most of the information is available via transthoracic electrocardiography, so cardiac catheterisation is rarely necessary. Patients >40 years of age often have coronary artery disease.
Result
assessment of left- and right-sided cardiac haemodynamics and coronary anatomy
cardiac MRI (preferred technique for evaluation of right ventricular size and function)
Test
Seldom required unless right heart function is determinant of operability.
Result
assessment of right heart ejection fraction
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer