Investigations
1st investigations to order
non-contrast CT scan
Test
Standard for initial evaluation of all patients with moderate or high risk for intracranial injury.[35] Subdural fluid collections are usually crescentic in shape and can cross suture lines.[38] Acute haematomas are hyperdense, subacute haematomas are usually hyperdense or isodense, and chronic haematomas are usually hypodense.[39] However, subdural haematomas (SDHs) that are isodense relative to the brain parenchyma can be hyperacute; for example, in a profoundly anaemic patient or in a patient with an arachnoid tear and a mixture of haemorrhage and cerebrospinal fluid.[38] There may be effacement of the underlying sulci or midline shift, effacement of cisterns or other signs of herniation, or skull fracture or other intracranial haematomas. Cerebral swelling may be manifested as the loss of grey-white matter distinction or gyral integrity. SDHs that have a hypodense 'swirl' inside them signify potential hyperacute haematoma with active bleeding.[40][41]
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CT scans of the brain of an 80-year-old man with a gait disorder and a progressive cognitive impairment dating back about 6 months, showing a bilateral chronic subdural haematoma up to the convexityAdapted from BMJ Case Rep. 2009;2009:bcr06.2008.0130 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CT scan of the brain of an 80-year-old man with a gait disorder and a progressive cognitive impairment dating back about 6 months, showing a bilateral chronic subdural haematoma up to the convexityAdapted from BMJ Case Rep. 2009;2009:bcr06.2008.0130 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CT scan of the brain of an 80-year-old man with a gait disorder and a progressive cognitive impairment dating back about 6 months, showing a bilateral chronic subdural haematoma up to the convexityAdapted from BMJ Case Rep. 2009;2009:bcr06.2008.0130 [Citation ends].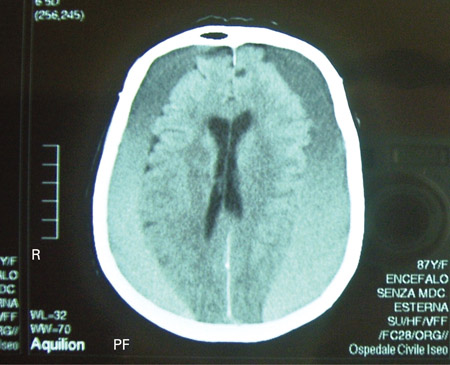
Result
subdural fluid collection
Investigations to consider
MRI scan
Test
Useful when there are persistent neurological deficits that remain unexplained after CT, especially in the subacute or chronic phase or in the absence of trauma history.[35] May identify differential diagnoses (e.g., lymphoma, metastasis, sarcoma, infection).
Similar results to CT scan. Intensities of fluid collection differ according to the age of the haematoma. Indicated as a follow-up study when there are persistent neurological deficits that remain unexplained after a head CT.[35]
Result
subdural fluid collection
plain skull x-ray
Test
Not sensitive or specific for intracranial haematomas.[35] May be useful for identifying skull fractures or the presence of intracranial shrapnel.
Result
possible skull fracture or presence of intracranial shrapnel
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer