Investigations
1st investigations to order
FBC
Test
Performed as baseline.
Result
elevated WBC
complete metabolic profile
Test
Performed as baseline.
Result
may be normal; may show hyponatraemia, elevated aspartate aminotransferase/alanine aminotransferase
chest x-ray
Test
To evaluate for lobar infiltrate. If infiltrate is absent, but clinical suspicion remains, laboratory tests should be ordered. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chest x-ray showing Legionella infection: right lower lobe infiltrate consistent with pneumonia (arrow). Legionella confirmed positive with urinary antigen testFrom the personal collection of Dr Forest W. Arnold; used with permission [Citation ends].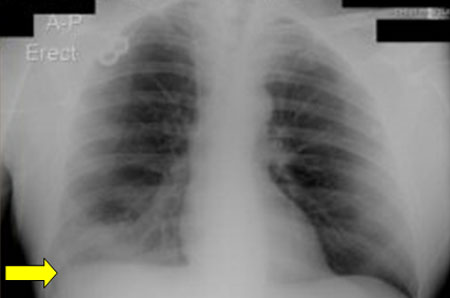 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chest x-ray (lateral) showing infection: posterior segment of lower lobe consistent with pneumonia; the area in the triangle is normally clear (black). confirmed with positive urinary antigen testFrom the personal collection of Dr Forest W. Arnold; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chest x-ray (lateral) showing infection: posterior segment of lower lobe consistent with pneumonia; the area in the triangle is normally clear (black). confirmed with positive urinary antigen testFrom the personal collection of Dr Forest W. Arnold; used with permission [Citation ends].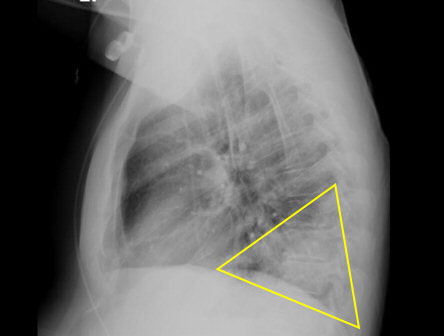 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: A portable anterior/posterior chest radiograph showing a right lower lobe infiltrate consistent with Legionnaire's diseaseFrom the personal collection of Dr Forest W. Arnold; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: A portable anterior/posterior chest radiograph showing a right lower lobe infiltrate consistent with Legionnaire's diseaseFrom the personal collection of Dr Forest W. Arnold; used with permission [Citation ends].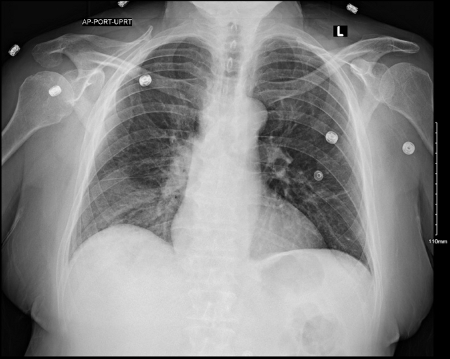
Result
Legionnaires' disease: lobar infiltrate; Pontiac fever: normal
CT abdomen
Test
To evaluate for lobar infiltrate. If infiltrate is absent, but clinical suspicion remains, laboratory tests should be ordered.
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: The superior aspect of a CT abdomen with contrast showing a right lower lobe, dense, lobar infiltrate consistent with Legionnaires' disease causing pneumonia with a small left pleural effusionFrom the personal collection of Dr Forest W Arnold; used with permission [Citation ends].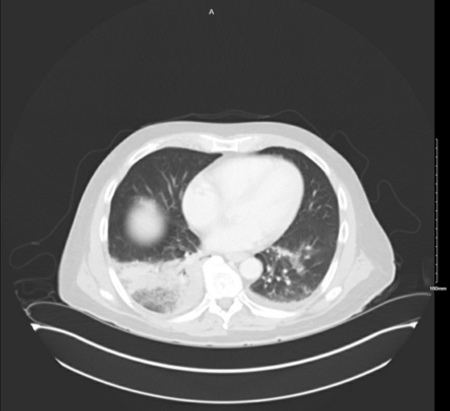
Result
Legionnaires' disease: lobar infiltrate; Pontiac fever: normal
urine antigen detection of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1
Test
Concentrated urine has better yield.[43]
Sensitivity 80%; specificity >99%.[44]
High sensitivity for detecting Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1, but lower ability to detect alternative species and serogroups.
Pooled sensitivity of 74%.[38]
Test may remain positive for weeks or months so cannot be used as a test of cure.
Result
positive detection of Legionella antigen
sputum Gram stain
Test
The Gram stain may be used to screen sputum specimens before culture is performed.
Result
visualisation of gram-negative coccobacilli suggestive of Legionella species, but usually there are large numbers of neutrophils but few, if any, organisms seen
cultures
Test
Cultures are taken of lower respiratory tract secretions, pleural fluid, or lung, blood, or extra-pulmonary tissue or fluids for Legionella species.
Special media and expertise required.
Sensitivity 20% to 95%; specificity 100%.[42]
Result
positive growth
Investigations to consider
Legionella pneumophila polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
Test
PCR can be used to detect Legionella species nucleic acid in lower respiratory tract specimens (e.g., sputum, bronchoalveolar lavage). Throat swabs can also be sent for PCR but the sensitivity is low.[41] PCR has the advantage of producing rapid results within hours and, unlike urine antigen testing, can detect all species and serogroups of Legionella. This makes it particularly useful for epidemiological typing, as well as for diagnosis in cases where urinary antigen testing is negative but clinical suspicion of Legionella infection remains high. It is highly sensitive and specific. However, its use may be limited by the fact that a significant proportion of patients with Legionnaires’ disease do not produce sputum. Induced sputum and bronchoscopic lavage may increase diagnostic yield in this situation.
Sensitivity 20% to 75%; specificity 90% to 95%.[45]
At present, there are no FDA-approved Legionella PCR assays available in the US.
Result
positive
Legionella pneumophila serology
Test
Optional laboratory test typically used in epidemiological studies. Rarely used in clinical practice. Legionella infections where the diagnosis is made using only serological methods no longer meet the case definitions for the purposes of public health action or surveillance in the UK.[39]
Sensitivity 20% to 70%; specificity 95% to 99%.[40][46]
Test has higher positive predictive value if paired acute and convalescent titres performed.[47]
Result
acute IgG, IgM, or IgA titres of ≥256 (suggestive) or ≥1024 (more suggestive); fourfold increase in IgG, IgM, or IgA between acute and convalescent titres
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer