Investigations
1st investigations to order
alkaline phosphatase (ALP)
Test
Suggestive of the presence of cholestasis (of which PBC is one cause) if alkaline phosphatase is of liver origin (isoenzymes or co-elevation of gamma-GT can be helpful in determining this if there is clinical doubt).
Result
elevated
gamma-glutamyl transferase (GTT)
Test
Suggestive of presence of cholestasis (of which PBC is one cause).
Result
elevated
bilirubin
Test
Suggestive (although not confirmatory) of disease progression with the presence of advanced fibrosis.
Result
Normal or elevated in advanced disease
alanine aminotransferase (ALT)
Test
Less than 10% of patients with PBC have a more inflammatory process than usual, and the presence of this inflammatory variant is confirmed by liver biopsy. Suspicion of this variant may be raised by a disproportionately elevated ALT.
Result
Normal or mildly elevated
serum albumin
Test
Suggestive (although not confirmatory) of impaired liver synthetic function compatible with the presence of advanced liver disease.
Result
Normal or decreased in advanced disease
antimitochondrial antibody (AMA) immunofluorescence
Test
Seen as diffuse staining throughout the cytoplasm. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Characteristic autoantibody patterns in primary biliary cholangitis. White arrow: antimitochondrial staining; red arrow: multiple nuclear dot ANA stainingFrom the collection of DEJ Jones; used with permission. [Citation ends].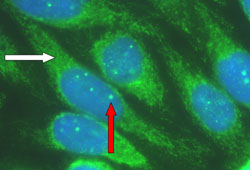
Use of immunofluorescence and ELISA will vary according to local practice.[25] Use of both methodologies is only needed in situations of clinical doubt.
Result
present
antinuclear antibody (ANA) immunofluorescence
Test
This pattern of staining of multiple dots within the nucleus, along with a nuclear rim staining pattern not seen in this example, is characteristic of PBC and must be distinguished from the diffuse nuclear staining pattern that is characteristic of autoimmune hepatitis and systemic lupus erythematosus. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Characteristic autoantibody patterns in primary biliary cholangitis. White arrow: antimitochondrial staining; red arrow: multiple nuclear dot ANA stainingFrom the collection of DEJ Jones; used with permission. [Citation ends].
Use of immunofluorescence and ELISA will vary according to local practice.[25] Use of both methodologies is only needed in situations of clinical doubt.
Result
staining pattern either antinuclear rim (indicates reaction with nuclear pore complex) or multiple nuclear dots (indicates reaction with Sp100 protein), or both
antipyruvate dehydrogenase complex-E2 ELISA
Test
Indicates presence of antimitochondrial antibody.
Titres of >1:40 are regarded as significant.
Use of immunofluorescence and ELISA will vary according to local practice.[25]
Result
present
anti-M2 ELISA
Test
Indicates presence of antimitochondrial antibody.
Titres of >1:40 are regarded as significant.
Use of immunofluorescence and ELISA will vary according to local practice.[25]
Result
present
antiglycoprotein-210 ELISA
Test
Indicates presence of antinuclear rim antinuclear antibody.
Titres of >1:40 are regarded as significant.
Use of immunofluorescence and ELISA will vary according to local practice.[25]
Result
present
anti-Sp100 ELISA
Test
Indicates presence of multiple nuclear dots antinuclear antibody.
Titres of >1:40 are regarded as significant.
Use of immunofluorescence and ELISA will vary according to local practice.[25]
Result
present
abdominal ultrasound scan
Test
Obstructive duct lesions must always be excluded radiologically before the diagnosis of PBC is made.[27]
Result
excludes obstructive lesion within visible bile ducts
magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP)
Test
Can be used as an alternative to ultrasound to detect bile duct stones and lesions causing extrahepatic obstruction, particularly of the distal bile duct.[15] Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) can be an alternative to MRCP for evaluation of distal biliary disease.[14][15]
Result
excludes obstructive lesion within visible bile ducts and hepatocellular carcinoma
Investigations to consider
serum immunoglobulin
liver biopsy
Test
Not usually needed to confirm the diagnosis.[14][15][30]
Liver biopsy should only be carried out if there is diagnostic uncertainty or concern about the presence of potentially corticosteroid-responsive inflammatory disease.
Result
bile duct lesions (biliary ductular cell disruption within inflamed portal tracts) and granulomata formation; later disease stages: bile duct loss (ductopenia) with progressive biliary fibrosis; a more inflammatory pattern with interface hepatitis can be seen in a minority of patients (<10%)
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer