Differentials
Common
Lumbar muscular strain/sprain
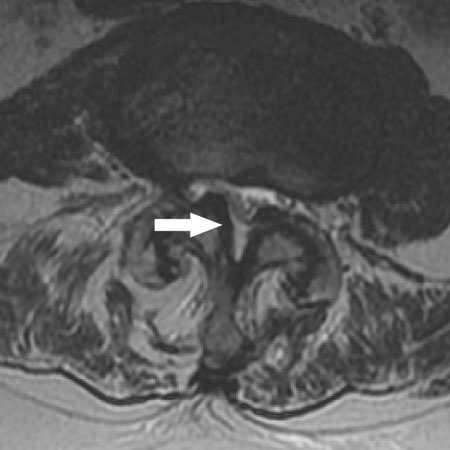
Herniated nucleus pulposus
History
radiating lower extremity pain in a dermatomal distribution; history of bowel or bladder dysfunction, bilateral sciatica, and saddle anaesthesia may be symptoms of severe compression of the cauda equina
Exam
1st investigation
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI):
herniated disc
More
Other investigations
- plain x-rays:
no abnormalities are normally found on plain x-rays
More
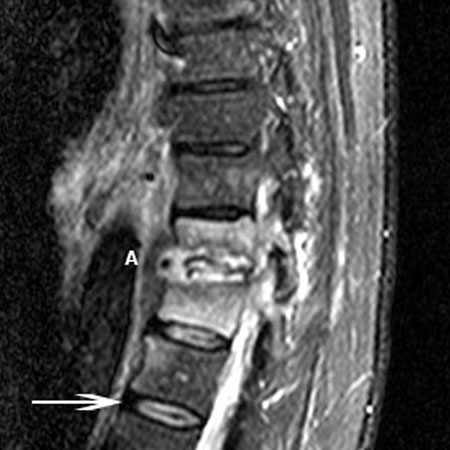
Spinal stenosis
History
intermittent pain radiating to the thigh or legs, worse with prolonged standing, activity, or lumbar extension; pain is typically relieved by sitting, lying down, and/or lumbar flexion; patient may describe intermittent burning, numbness, heaviness, or weakness in their legs, unilateral or bilateral radicular pain, motor deficits, bowel and bladder dysfunction, and back and buttock pain with standing and ambulation
Exam
patients walk with a forward flexed gait; patients with vascular claudication have diminished pulses and typical skin changes, such as mottled discolouration, thinning and shiny skin
1st investigation
- magnetic resonance imaging:
spinal stenosis; hypertrophy of the facet joints and/or ligamentum flavum with corresponding decrease in spinal canal diameter dimension
More
Other investigations
- plain x-rays:
degenerative arthritis; diffuse osteophyte formation normally seen with an accompanying degenerative spondylolisthesis or scoliosis
More
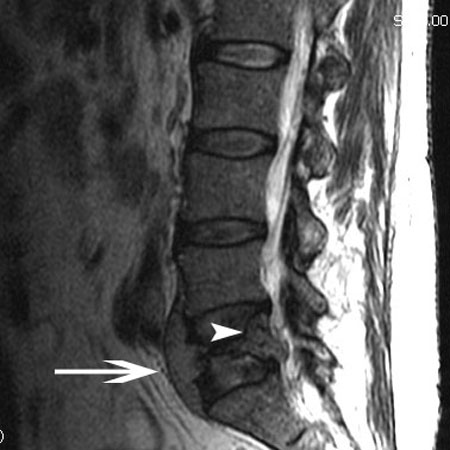
Compression fracture
History
typically history of trauma, although acute event not always recalled; pain at rest and at night, previous history of fragility fractures (e.g., distal radius, hip or other vertebral compression fractures); history of osteoporosis or at risk of osteoporosis (i.e., older age, post menopausal, prolonged steroid therapy)
Exam
tenderness to palpation over the midline; increased kyphosis, normal neurological examination unless there is retropulsion of bone into the neural elements, such as in burst fractures
1st investigation
- plain x-rays:
wedging of the vertebral bodies, typically anteriorly; kyphotic deformity; only the anterior half of the vertebral body is involved in compression fractures
More
Degenerative disc disease or facet arthropathy
History
discogenic symptoms worsen with forward flexion, coughing/sneezing, or heavy lifting; facet mediated pain is typically worse with extension
Exam
decreased range of motion due to pain and mild tenderness on palpation; pain is reproduced with flexion in discogenic pain and extension with facet arthropathy
1st investigation
- no initial test:
clinical diagnosis
More
Other investigations
- magnetic resonance imaging:
degenerative disc disease: loss of disc height, end plate collapse, and usually decreased T2 signal in the disc; annular tear; facet arthropathy: hypertrophy of the facet and possible T2 signal in the joint
More - plain x-rays:
degenerative arthritis and diffuse osteophyte formation
More
Sacroiliitis
History
low back pain, may be lower extremity pain
Exam
1st investigation
- none:
clinical diagnosis
Other investigations
- plain x-rays:
no other abnormalities normally seen
- diagnostic local anaesthetic block injection to sacroiliac joint with C-arm fluoroscopic guidance:
significant decrease in pain after sacroiliac joint injection
Uncommon
Cauda equina syndrome
History
bowel or bladder or sexual dysfunction, back pain with or without sciatica; symptoms may come on gradually; history of lumbar disc herniation, spinal stenosis, spinal injury, spinal neoplasm (primary or metastasis), infection (e.g., tuberculosis), spinal surgery
Exam
sensory changes in saddle or perianal area; sensory changes or numbness in the lower limbs; lower limb weakness, reduction or loss of reflexes in lower limbs; reduced anal tone
1st investigation
- MRI with or without contrast:
compression of the cauda equina
More
Spinal cord compression
History
localised back pain, with or without radicular pain; history of spine trauma, vertebral compression fracture, disk herniation, tumor or infection; altered sensation or hemisensory loss; weakness; constipation, urinary retention
Exam
altered sensation below a certain level or hemisensory loss; hemiplegia/hemiparesis, paraplegia/paraparesis or tetraplegia/tetraparesis; hyporeflexia (hyperreflexia can occur early if the cause is malignancy), positive Babinski sign; decreased anal tone
1st investigation
- MRI spine:
compression of the spinal cord
More
Other investigations
- CT spine:
compression of the spinal cord
More
Spondylolysis and/or spondylolisthesis
History
most are asymptomatic; pain in the lower back with occasional radiation to the posterior thigh and aggravated by extension
Exam
1st investigation
- plain x-rays:
linear lucency in the pars interarticularis
More
Vertebral discitis/osteomyelitis
History
infection should be considered for patients with a history of fever, weight loss, and non-mechanical back pain (i.e., pain that occurs even without motion, particularly at rest and at night); history of intravenous drug use, immunosuppression, or diabetes
Exam
generalised appearance of malaise; fever; localised tenderness present particularly with percussion; neurological findings absent
1st investigation
Malignancy
History
history of malignancy (breast, lung, prostate, thyroid, kidney), age >50 years, back pain at night and at rest; may have neurological deficits if tumour destruction is extensive and causes neurological compression
Exam
generalised systemic symptoms including fevers/chills, weight loss, and malaise; focal tenderness and/or neurological deficits may be present depending on tumour size and location
1st investigation
- magnetic resonance imaging:
either a lytic or blastic lesion with varying T2 signal intensity; lesion typically does not cross the end plate, but soft tissue extension may be present
More
Inflammatory spondyloarthropathy
History
male predominance in ankylosing spondylitis, early-morning stiffness, nocturnal back pain, fatigue, weight loss, diffuse nonspecific pain radiating bilaterally to buttocks; pain improves after physical activity or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; may have symptoms of dactylitis, enthesitis, uveitis or psoriasis; may have family history of arthritis or psoriasis; history of inflammatory bowel disease may be suggestive of enteropathic arthritis; history of recent genitourinary infection
Exam
axial spondyloarthropathy or ankylosing spondylitis: stiffness of spine with kyphosis, limited range of movement of lower spine, tenderness on palpation; extra-articular signs may be present, including enthesitis, uveitis, dactylitis, psoriasis, crohn’s disease, and ulcerative colitis
1st investigation
- plain x-ray sacroiliac joints:
erosion of sacroiliac joint (squaring of lumbar vertebrae) and later narrowing and fusion (bamboo spine) is suggestive of ankylosing spondylitis
More
Connective tissue disease
History
arthralgias, polyarthritis, systemic symptoms of fever, weight loss, and fatigue
Exam
evidence of organ involvement (e.g., rash, lymphadenopathy, wheeze, signs of malabsorption, joint tenderness, joint effusion and swelling, signs of uveitis, conjunctivitis)
1st investigation
Other investigations
- chest x-ray:
normal; mediastinal lymphadenopathy; interstitial lung disease; pericardial effusion
- plain x-ray of spine:
may be evidence of rheumatoid arthritis
Scoliosis
History
back pain, postural asymmetry, adolescent patient
Exam
lateral curvature of spine in coronal plane; paraspinal and rib prominences accentuated by forward flexion; asymmetric scapular prominence; normal neurologic examination
1st investigation
- none:
clinical diagnosis
Other investigations
- whole spine x-ray:
spine curvature >10 degrees in the coronal plane
More
Abdominal aortic aneurysm
History
sudden onset of intermittent or continuous abdominal pain, radiating to the back; patient may collapse; older age; history of cardiovascular disease
Exam
pulsatile abdominal mass, hypotension or hypertension, tachycardia
1st investigation
- abdominal ultrasound:
extent and size of aneurysm
Other investigations
- computed tomography angiography:
clearly defines aneurysm and involvement of visceral arteries
More
Acute pancreatitis
History
sudden onset of epigastric pain; radiates to back; may be relieved by sitting forwards; associated with nausea and vomiting; history of alcohol use or gallstones
Exam
tachycardia, fever, jaundice, tenderness/guarding of abdomen
1st investigation
Other investigations
- ultrasound:
may show pancreatic inflammation, peripancreatic stranding, calcifications, or fluid collections
More - contrast-enhanced computed tomography:
fluid collections; pseudocysts; abscess
More - magnetic imaging/magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRI/MRCP):
findings may include stones, tumours, diffuse or segmental enlargement of the pancreas with irregular contour and obliteration of the peripancreatic fat, necrosis, or pseudocysts
More
Pyelonephritis
History
urinary symptoms of dysuria, frequency, and hesitancy; flank pain may radiate to back; fever, chills, fatigue
Exam
flank or costovertebral tenderness
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
pyuria, microscopic haematuria
- urine culture:
positive
Other investigations
- renal ultrasound:
gross structural abnormalities; hydronephrosis; stones; perirenal fluid collections
More - contrast-enhanced computed tomography:
altered renal parenchymal perfusion; altered excretion of contrast; perinephric fluid; non-renal disease
More - MRI:
can be normal with mild infection; with severe infection, parts of the kidney may appear oedematous and of lower attenuation; other findings may include renal calculi or gas within the collecting system; perinephric stranding can be seen
More
Renal colic
History
severe, acute flank pain that may radiate to the ipsilateral groin; associated nausea and vomiting; history of volume depletion or stone-inducing medications (e.g., antacids, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, sodium- and calcium-containing medications, vitamins C and D, indinavir)
Exam
flank or costovertebral angle tenderness; may have macroscopic haematuria
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
microscopic haematuria
More - non-contrast computed tomography:
calcification seen in renal collecting system or ureter
- FBC:
normal or elevated WBC count
- serum electrolytes, urea and creatinine:
normal or deranged
Other investigations
- renal ultrasound:
calcification seen within urinary tract
Peptic ulcer disease
History
epigastric, burning pain; radiates to back; usually occurs in association with meals; may be relieved by antacids; haematemesis or melaena in advanced disease
Exam
epigastric tenderness, may be melaena on rectal examination
1st investigation
- FBC:
microcytic anaemia; elevated WBC count
- Helicobacter pylori test:
may be positive
- plain abdominal x-ray:
may see abdominal free air on erect abdominal film if perforation present. Images of both flat (supine) and upright (erect) position are taken.
More
Other investigations
- upper gastrointestinal endoscopy:
detects site of bleeding and ulceration
More - upper gastrointestinal series with water-soluble contrast:
extravasation of contrast from stomach
Spinal epidural abscess
History
focal spinal process pain, often with paravertebral spasm; pain is increased with weight-bearing and is not relieved by rest; history of diabetes mellitus, intravenous drug use, HIV infection, immune suppression, recent invasive procedures (e.g., previous spinal surgery or trauma, previous neuraxial anaesthesia associated with indwelling [intrathecal/epidural] catheter placement), dialysis, alcohol misuse; existing infections (e.g., infective endocarditis, urinary tract infection) may be a source of infection by haematogenous spread; focus of pre-existing local infection should also be ascertained, as direct extension from vertebral osteomyelitis, a psoas abscess, or a retropharyngeal abscess may be the source
Exam
fever with sweats and rigors or afebrile; signs and symptoms of neurological loss; weakness of extremities is common and may indicate impending motor weakness; sensory disturbance, abnormal reflexes (ranging from hyperreflexia to reduced or absent responses), and isolated sphincter dysfunction
1st investigation
Herpes zoster infection
History
burning, stinging or stinging pain in dermatomal distribution; pruritus, rash; risk factors (older age, immunosuppression)
Exam
rash in dermatomal distribution which does not cross the midline, initially erythematous and maculopapular, later vesicular
1st investigation
- none:
clinical diagnosis
Other investigations
- polymerase chain reaction for viral DNA:
positive for varicella zoster DNA
Retroperitoneal bleed
History
symptoms may be vague; groin, lower abdominal or back pain; history of risk factors (e.g., recent anticoagulation use, recent history of cardiac or femoral angiography, recent obstetric procedure in women of child-bearing age)
Exam
unexplained tachycardia; tenderness in lower abdomen on side of bleed; may be bruising of flank; diaphoresis if severe; profound hypotension with decreasing levels of consciousness if shock present
1st investigation
- basic test panel (FBC, serum electrolytes, blood glucose, serum LFTs, coagulation profile, group and save):
low Hb; INR may be raised
- ECG:
normal, or tachycardia
Other investigations
- CT abdomen:
haematoma may be visualised
- CT angiogram:
may demonstrate active bleeding site if bleeding is ongoing
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer