Investigations
1st investigations to order
urine or serum pregnancy test
Test
Confirms pregnancy.[40]
Result
positive
high resolution transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS)
Test
Once pregnancy is confirmed, TVUS is used to determine the location of the pregnancy.[40]
If an intrauterine gestation is visualised, which can be either viable or non-viable, the likelihood of having an ectopic pregnancy is extremely low, with the exception of heterotopic pregnancy.[45]
An ectopic pregnancy is visualised on TVUS and the diagnosis is made directly.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Ultrasound image of ectopic pregnancy showing the 'bagel' signFrom the collection of Dr Melissa Fries; used with permission [Citation ends].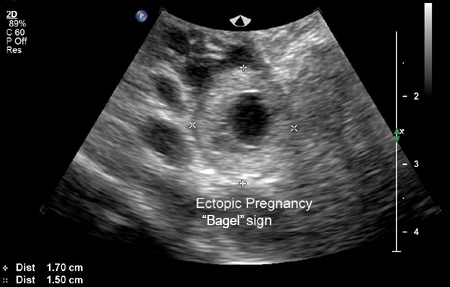 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Ultrasound image of ectopic pregnancy showing the 'bagel' signFrom the collection of Dr Melissa Fries; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Ultrasound image of ectopic pregnancy showing the 'bagel' signFrom the collection of Dr Melissa Fries; used with permission [Citation ends].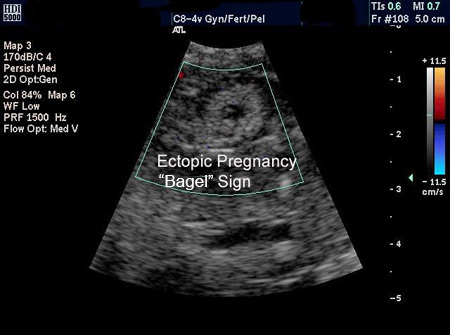
An adnexal mass moving separately to the ovary, sometimes referred to as the 'sliding sign', with an empty gestational sac sometimes described as a 'tubal ring' or 'bagel sign', and a complex, inhomogeneous adnexal mass, moving separate to the ovary, are highly suggestive of an ectopic pregnancy, but not diagnostic.[63]
However, in a significant number of cases, neither an intrauterine nor an ectopic pregnancy can be visualised on ultrasound, resulting in the so-called pregnancy of unknown location.[48]
Using TVUS, an intrauterine pregnancy should be seen by 5 weeks after the last menstrual period.[64]
If an intrauterine pregnancy cannot be confirmed when discriminatory human chorionic gonadotrophin levels are reached (3000-3500 mIU/mL]), there is an increased risk that the pregnancy is ectopic. However, it may also represent a failing intrauterine pregnancy.
Result
no intrauterine pregnancy detected; ectopic pregnancy visualised
transabdominal ultrasound
Test
Less sensitive than transvaginal ultrasound; likely to detect intrauterine pregnancy by 6 weeks after last menstrual period or when discriminatory human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG) levels for transabdominal ultrasound have reached 4000-6500 IU/L (4000-6500 mIU/mL).
If intrauterine location is not identified after discriminatory hCG level is reached, there is an increased risk that the pregnancy is ectopic. However, it may also represent a failing intrauterine pregnancy.
Result
no intrauterine pregnancy detected
Investigations to consider
serial serum human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG)
Test
Ordered to confirm pregnancy or if transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS) does not confirm an intrauterine pregnancy.
The expected rise in serum hCG in a normal pregnancy can depend on the initial values. If the initial hCG level is <1500 IU/L (<1500 mIU/mL), then an increase of 49% or higher would be expected over 2 days; whereas, with an initial level of >3000 IU/L (>3000 mIU/mL), the expected increase would be ≥33% over 2 days.[53] In 99% of viable intrauterine pregnancies, there will be a greater rise in hCG levels over a 48-hour period than these minimum thresholds; a lower rate of increase should raise suspicion of an ectopic pregnancy or early pregnancy loss but is not diagnostic of non-viability.[53][54][65] It is important to also remember that neither an expected rise in serum hCG nor falling levels rule out the possibility of ectopic pregnancy.[55] Caution is advised when interpreting the hCG result, as one study revealed that up to 27% of women diagnosed with an ectopic pregnancy had hCG curves resembling a normal pregnancy.[56]
When level is well above discriminatory level of 3000-3500 IU/L (3000-3500 mIU/mL) and there is no sign of intrauterine gestation on TVUS, a viable intrauterine gestation is relatively unlikely and successive serum quantitative hCG can be used to differentiate between an ectopic pregnancy and a failing (non-viable) intrauterine gestation (miscarriage).
A steady decrease in hCG values (i.e., a decrease of 50% in 48 hours) suggests a failing pregnancy (miscarriage). This could be intrauterine, but may also represent a spontaneously resolving ectopic pregnancy.[47][58]
On the other hand, suboptimal increase (i.e., <49% rise in 48 hours if the initial hCG level is <1500 IU/L [<1500 mIU/mL], <40% rise in 48 hours for an initial hCG level of between 1500 and 3000 IU/L (1500 and 3000 mIU/mL) or <33% rise in 48 hours if the initial hCG level is >3000 IU/L [>3000 mIU/mL]) or plateauing of hCG values suggests a non-viable pregnancy, including a potential ectopic pregnancy.[47][59]
A third hCG in a stable woman and early ultrasound may decrease intrauterine pregnancy misclassification.[66] It is recommended that, if discriminatory levels are used to diagnose ectopic pregnancy, a conservatively high value should be used (e.g., 3500 IU/L [3500 mIU/mL]) to avoid misdiagnosis.[47]
Result
<49% rise in 48 hours if the initial hCG level is <1500 IU/L (<1500 mIU/mL), <40% rise in 48 hours for an initial hCG level of between 1500 and 3000 IU/L (1500 and 3000 mIU/mL) or <33% rise in 48 hours if the initial hCG level is >3000 IU/L (>3000 mIU/mL) or plateau of level
uterine aspiration
Test
Can be carried out if the possibility of a viable pregnancy has been reasonably excluded.
Used to distinguish early intrauterine pregnancy loss from ectopic pregnancy by identifying the presence or absence of intrauterine chorionic villi. The presence of chorionic villi confirms a failed intrauterine pregnancy. If chorionic villi cannot be found, then human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG) levels should be monitored, with the first measurement taken 12 to 24 hours after aspiration. A plateau (a less than 10% to 15% decline) or increase in hCG post-procedure suggests that evacuation was incomplete or a non-visualised ectopic pregnancy, and further treatment is warranted.[47]
Performance of a uterine evacuation in women with a persistent pregnancy of unknown location will decrease time to resolution by up to 6 days.[65]
Result
intrauterine chorionic villi absent
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer