Images and videos
Images
Congenital heart disease
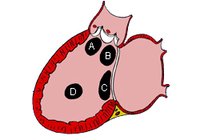
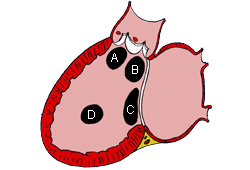
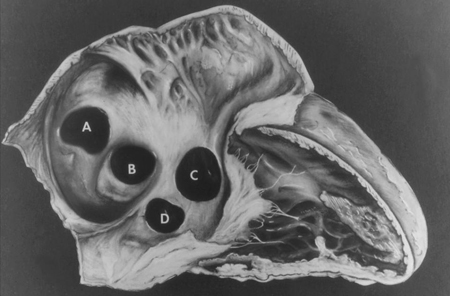
Subtypes of ventricular septal defects: (A) outlet; (B) perimembranous; (C) inlet; (D) muscular
Mayo Clinic Foundation
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Congenital heart disease
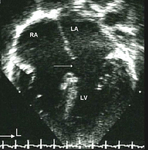
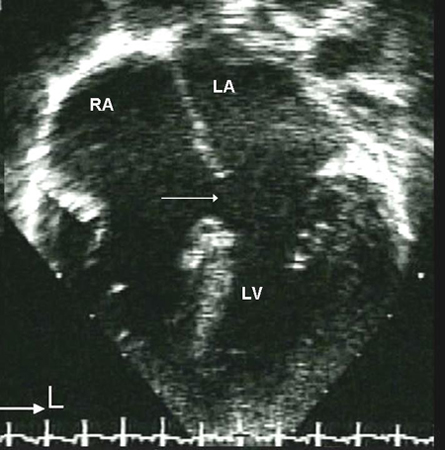
Apical 4-chamber echocardiographic image of an ostium primum ASD (arrow). (RA) right atrium; (LA) left atrium; (LV) left ventricle
Image courtesy of Patrick W. O'Leary, MD
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Congenital heart disease
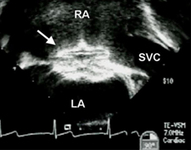
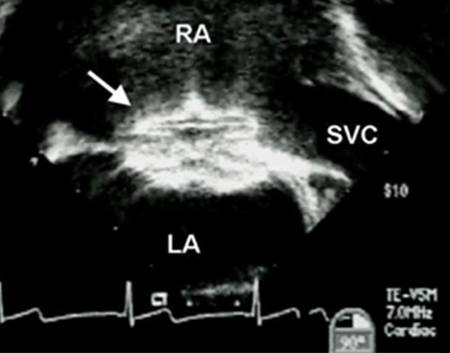
Transesophageal echocardiographic image of an ASD occluder device (arrow). (RA) right atrium; (LA) left atrium; (SVC) superior vena cava
Image courtesy of Patrick W. O'Leary, MD
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Congenital heart disease
Subtypes of atrial septal defects: (A) sinus venosus; (B) ostium secundum; (C) ostium primum; (D) unroofed coronary sinus
Mayo Clinic Foundation
See this image in context in the following section/s:

Congenital heart disease
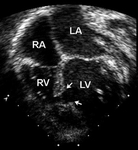
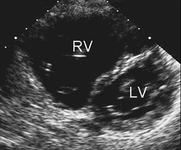
Apical 4-chamber echocardiographic image demonstrating right ventricular enlargement in a patient with an ASD. (RA) right atrium; (RV) right ventricle; (LV) left ventricle
Image courtesy of Patrick W. O'Leary, MD
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Congenital heart disease
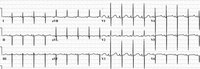
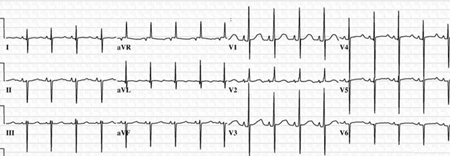
12-lead ECG in an infant with complete AVSD; the ECG is significant for left axis deviation
Mayo Clinic Foundation
See this image in context in the following section/s:

Congenital heart disease
Parasternal short axis echocardiographic image demonstrating right ventricular enlargement in a patient with an ASD. (RV) right ventricle; (LV) left ventricle
Image courtesy of Patrick W. O'Leary, MD
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Congenital heart disease
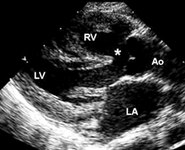
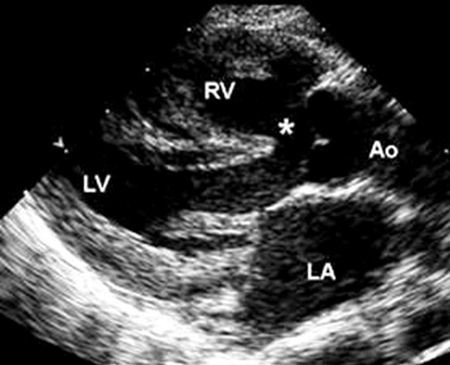
Parasternal long axis echocardiographic image in a patient with tetralogy of Fallot. The aorta (Ao) overrides the VSD (*). (LA) left atrium; (RV) right ventricle; (LV) left ventricle
Image courtesy of Patrick W. O'Leary, MD
See this image in context in the following section/s:

Congenital heart disease
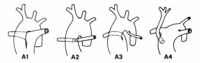
Subtypes of truncus arteriosus with ventricular septal defect (type A): Type A1: main pulmonary artery is present and bifurcates into the left and right pulmonary arteries Type A2:right and left branch pulmonary arteries arise from a common trunk. Type A3: One branch pulmonary artery arises from the common trunk and the other is absent/arises from a PDA or the aorta. Type A4: Truncus with aortic arch hypoplasia, coarctation or interrupted aortic arch and a large PDA
Calder L et al. Am Heart J 1976 Jul;92(1):23-38; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Congenital heart disease
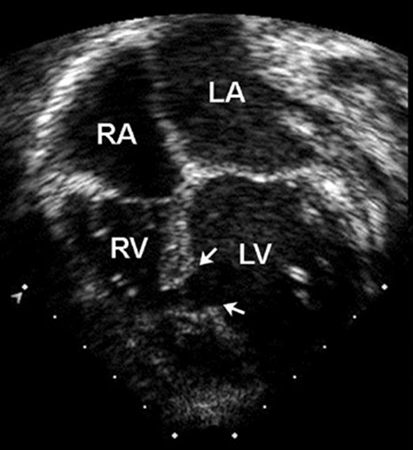
Apical 4-chamber echocardiographic image of a muscular VSD (arrow). (RA) right atrium; (LA) left atrium; (RV) right ventricle; (LV) left ventricle
Image courtesy of Patrick W. O'Leary, MD
See this image in context in the following section/s:

Congenital heart disease
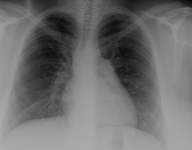
CXR demonstrating pulmonary overcirculation
Mayo Clinic Foundation
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Congenital heart disease
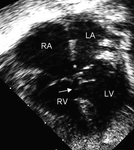
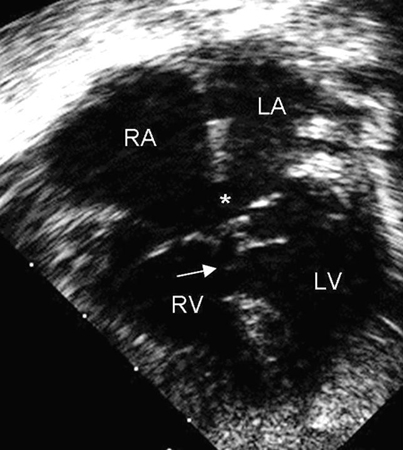
Apical 4-chamber echocardiographic image of complete AVSD. Note the ostium primum ASD (*) and the contiguous inlet VSD (arrow). (RA) right atrium; (LA) left atrium; (RV) right ventricle; (LV) left ventricle
Image courtesy of Patrick W. O'Leary, MD
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer