Superconducting Circuit Technology Developments
Communication and information technology have long been supported by semiconductor integrated circuits (ICs), such as complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS) technology. One of the advantages of CMOS is its high density; the transistor size has become smaller year by year, following Moore's law. However, CMOS technology is approaching the limit of physical miniaturization and, in turn, the limit at which switching energy can be reduced through scaling. For applications requiring large computing facilities such as data centers, supercomputers, and information network infrastructure, it is necessary to develop a new circuit technology that is more energy-efficient than CMOS.
Superconductor ICs can be that solution. In particular, the adiabatic quantum-flux-parametron (AQFP) circuit is an emerging technology that can operate at gigahertz-order speeds with extremely low energy dissipation via adiabatic switching. In an article published in IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, researchers introduce two types of algorithms to calculate multiplication results: array and Wallace-tree.
The researchers investigated the implementation of multipliers in AQFP technology to further develop it for practical use cases. The multiplication operation is vital in signal and image processing, GPUs for graphics acceleration, and tensor cores for artificial intelligence (AI) acceleration. Addressing cybersecurity and intelligent computing in today's information-driven society are essential domains where AQFP technology can potentially improve energy efficiency. This is a first step toward exploring the design space for using AQFP circuits in signal processing, encryption/cryptography, graphics, and AI acceleration applications.
Multiplication Algorithms
The researchers begin by explaining their multiplication approach, emphasizing the importance of considering how to add all partial products efficiently to improve the performance of the multiplier. They then introduce the two types of multiplication algorithms explored in this work:
Array Multiplication Algorithm
The array type is the most fundamental multiplication algorithm. Its advantage is that its structure is simple from a physical design perspective, and it is easy to expand to larger data word sizes by replicating the array's structures. However, the disadvantage is that the circuit's area and latency tend to be larger.
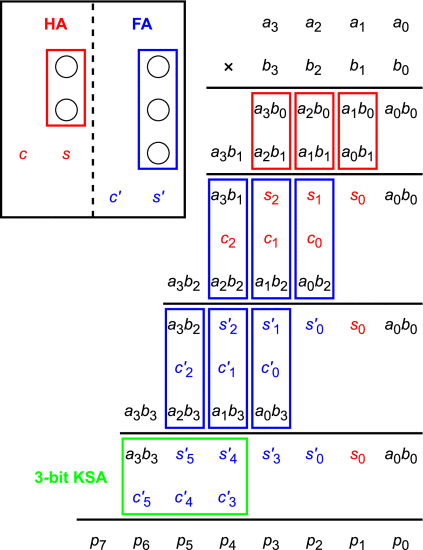
Overview of the array-type multiplication algorithm
Wallace-Tree Multiplication Algorithm
To resolve this latency problem, the Wallace-tree algorithm was suggested. It is possible to lower the latency of the circuit compared to the array type thanks to the efficient compression of the partial products performed by the Wallace tree.
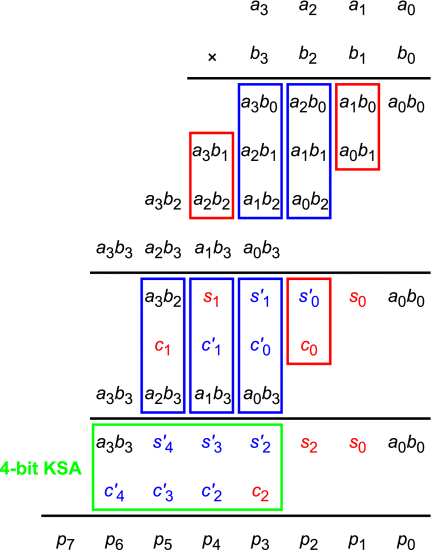
Overview of the Wallace-tree-type multiplication algorithm
The researchers designed both the array and Wallace-tree-type 4-bit multipliers implemented in AQFP logic by hand, and they outlined the specifics of the circuit fabrication process.
Discussion & Future Steps
This article describes the design and measurement results of 4-bit multipliers implemented in AQFP technology for the first time. Compared with rapid single-flux-quantum (RSFQ) multipliers, AQFP multipliers are superior in energy efficiency by at least five orders of magnitude.
To realize larger multiplier designs, various metrics of AQFP circuits, particularly latency and area, need further improvement. The researchers posit that implementing a more efficient multiplication algorithm is one solution. They plan to investigate the bit scaling of AQFP multipliers and consider this modern algorithm the next implementation candidate.
Another solution for area reduction is advancing the target process for AQFP technology. The 3-D integration of superconductor circuits can reduce the circuit's footprint. Furthermore, low-latency clocking schemes, such as power-dividing or delay-line clocking, can improve the circuit's latency instead of four-phase clocking.
The researchers' successful demonstration is a first step toward building extremely energy-efficient multipliers for highly in-demand applications such as cybersecurity and AI.
Interested in learning more about Circuit Technology? The IEEE Xplore Digital Library offers over 400,000 publications on Circuit Technology.
Interested in acquiring full-text access to this collection for your entire organization? Request a free demo and trial subscription for your organization.



