The management of patients with rib fractures is dependent on the age of the patient, number of ribs fractured, and concomitant injuries. A patient with multiple injuries will require evaluation by the appropriate specialists. With chest wall injuries, the main goal is to determine the extent of injuries to the thoracic cage and other organ systems.
Older patients and those with >2 rib fractures are at a higher risk of pulmonary complications such as atelectasis, poor oxygenation, and respiratory compromise.[27]Brasel KJ, Moore EE, Albrecht RA, et al. Western trauma association critical decisions in trauma: management of rib fractures. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2017 Jan;82(1):200-3.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27779590?tool=bestpractice.com
Admission for pain control, pulmonary toilet (mucus and secretion clearance techniques), deep breathing, early mobilization and observation is therefore warranted.[27]Brasel KJ, Moore EE, Albrecht RA, et al. Western trauma association critical decisions in trauma: management of rib fractures. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2017 Jan;82(1):200-3.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27779590?tool=bestpractice.com
[42]Battle C, Pelo C, Hsu J, et al. Expert consensus guidance on respiratory physiotherapy and rehabilitation of patients with rib fractures: an international, multidisciplinary e-Delphi study. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2023 Apr 1;94(4):578-83.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10045972
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36728349?tool=bestpractice.com
Because of the increased morbidity and mortality in this subgroup, transfer to a center that has either a pulmonary critical care or a trauma team may be indicated.
Single rib fractures without associated injuries are often managed by pain control, physical therapy, and mobilization. It is important to remember that even single rib fractures can be associated with significant morbidity and mortality, particularly in frail, older patients.[43]Kishawi SK, Ho VP, Bachman KC, et al. Are we underestimating the morbidity of single rib fractures? J Surg Res. 2021 Dec;268:174-80.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8678162
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34329822?tool=bestpractice.com
Stress fractures, which most often occur in athletes, are initially treated with periods of rest, analgesia, and activity modification until symptoms resolve.[44]Reeder MT, Dick BH, Atkins JK, et al. Stress fractures: current concepts of diagnosis and treatment. Sports Med. 1996 Sep;22(3):198-212.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8883216?tool=bestpractice.com
Analgesia
Pain is imperative to treat as it improves pulmonary function and decreases the risk of pulmonary complications such as atelectasis, poor oxygenation, and respiratory compromise as well as reducing the risk of pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), and respiratory failure.[27]Brasel KJ, Moore EE, Albrecht RA, et al. Western trauma association critical decisions in trauma: management of rib fractures. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2017 Jan;82(1):200-3.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27779590?tool=bestpractice.com
[45]American College of Surgeons. Best practices guideline for acute pain management in trauma patients. Nov 2020 [internet publication].
https://www.facs.org/media/exob3dwk/acute_pain_guidelines.pdf
Individualized multimodal analgesia based on age, level of pain, and extent of the injury is recommended for patients with multiple fractured ribs.[45]American College of Surgeons. Best practices guideline for acute pain management in trauma patients. Nov 2020 [internet publication].
https://www.facs.org/media/exob3dwk/acute_pain_guidelines.pdf
[46]Karmakar MK, Ho AM. Acute pain management of patients with multiple fractured ribs. J Trauma. 2003 Mar;54(3):615-25.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12634549?tool=bestpractice.com
Start scheduled analgesia as soon as possible with acetaminophen and a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) such as ibuprofen (or, if regional block is likely to be needed, select a cyclo-oxygenase-2 [COX-2] inhibitor such as celecoxib to avoid platelet inhibition).[45]American College of Surgeons. Best practices guideline for acute pain management in trauma patients. Nov 2020 [internet publication].
https://www.facs.org/media/exob3dwk/acute_pain_guidelines.pdf
Other analgesics that may be used include muscle relaxants and oral opioids, with escalation to intravenous opioids and patient-controlled analgesia, as needed (useful for breakthrough pain in particular).[45]American College of Surgeons. Best practices guideline for acute pain management in trauma patients. Nov 2020 [internet publication].
https://www.facs.org/media/exob3dwk/acute_pain_guidelines.pdf
Increased emphasis on nonopioid options such as NSAIDs, acetaminophen, gabapentin, lidocaine topical patches, and the muscle relaxant methocarbamol (i.e., “multimodal analgesia”) may reduce opioid use.[45]American College of Surgeons. Best practices guideline for acute pain management in trauma patients. Nov 2020 [internet publication].
https://www.facs.org/media/exob3dwk/acute_pain_guidelines.pdf
[47]Burton SW, Riojas C, Gesin G, et al. Multimodal analgesia reduces opioid requirements in trauma patients with rib fractures. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2022 Mar 1;92(3):588-96.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8866226
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34882599?tool=bestpractice.com
[48]Martin TJ, Eltorai AS, Dunn R, et al. Clinical management of rib fractures and methods for prevention of pulmonary complications: a review. Injury. 2019 Jun;50(6):1159-65.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31047683?tool=bestpractice.com
A range of analgesia may be used for patients with complicated, multiple, or bilateral rib fractures, including regional nerve blocks (e.g., serratus anterior, paravertebral or intercostal blocks) or thoracic epidural anesthesia.[45]American College of Surgeons. Best practices guideline for acute pain management in trauma patients. Nov 2020 [internet publication].
https://www.facs.org/media/exob3dwk/acute_pain_guidelines.pdf
There are many options for regional anesthesia, which can be tailored to the patient. Early use of regional anesthesia can avoid the potential complications associated with opioid use.[45]American College of Surgeons. Best practices guideline for acute pain management in trauma patients. Nov 2020 [internet publication].
https://www.facs.org/media/exob3dwk/acute_pain_guidelines.pdf
Epidural analgesia improved pain relief compared with other analgesic interventions in one meta-analysis.[27]Brasel KJ, Moore EE, Albrecht RA, et al. Western trauma association critical decisions in trauma: management of rib fractures. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2017 Jan;82(1):200-3.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27779590?tool=bestpractice.com
[49]Peek J, Smeeing DPJ, Hietbrink F, et al. Comparison of analgesic interventions for traumatic rib fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2018 Feb 6;45(4):597-622.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6689037
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29411048?tool=bestpractice.com
However, further meta-analyses variously report that, compared with other analgesic modalities, epidural anesthesia does not significantly reduce mortality, intensive care unit (ICU) or hospital length of stay, length of mechanical ventilation, or pulmonary complications in patients with multiple traumatic rib fractures.[50]Carrier FM, Turgeon AF, Nicole PC, et al. Effect of epidural analgesia in patients with traumatic rib fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Can J Anaesth. 2009 Mar;56(3):230-42.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19247744?tool=bestpractice.com
[49]Peek J, Smeeing DPJ, Hietbrink F, et al. Comparison of analgesic interventions for traumatic rib fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2018 Feb 6;45(4):597-622.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6689037
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29411048?tool=bestpractice.com
A lidocaine topical patch can be an alternative to regional anesthesia.[45]American College of Surgeons. Best practices guideline for acute pain management in trauma patients. Nov 2020 [internet publication].
https://www.facs.org/media/exob3dwk/acute_pain_guidelines.pdf
[51]Cheng YJ. Lidocaine skin patch (Lidopat® 5%) is effective in the treatment of traumatic rib fractures: a prospective double-blinded and vehicle-controlled study. Med Princ Pract. 2016;25(1):36-9.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5588305
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26539836?tool=bestpractice.com
[52]Johnson M, Strait L, Ata A, et al. Do lidocaine patches reduce opioid use in acute rib fractures? Am Surg. 2020 Sep;86(9):1153-8.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32812770?tool=bestpractice.com
Also consider nonpharmacologic alternatives, particularly for uncomplicated rib fractures (e.g., positioning, transcutaneous electrical stimulation, and ice).[45]American College of Surgeons. Best practices guideline for acute pain management in trauma patients. Nov 2020 [internet publication].
https://www.facs.org/media/exob3dwk/acute_pain_guidelines.pdf
[53]Oncel M, Sencan S, Yildiz H, et al. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation for pain management in patients with uncomplicated minor rib fractures. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2002 Jul;22(1):13-7.
http://ejcts.oxfordjournals.org/content/22/1/13.long
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12103366?tool=bestpractice.com
[54]Hsu JR, Mir H, Wally MK, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for pain management in acute musculoskeletal injury. J Orthop Trauma. 2019 May;33(5):e158-82.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6485308
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30681429?tool=bestpractice.com
Oxygen
Administer oxygen as indicated to treat hypoxia.[55]Williams A, Bigham C, Marchbank A. Anaesthetic and surgical management of rib fractures. BJA Educ. 2020 Oct;20(10):332-40.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7807920
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33456914?tool=bestpractice.com
Impaired oxygenation can be due to impaired effort of ventilation following chest wall pain or be indicative of underlying pneumothorax, hemothorax, or pulmonary contusion.[27]Brasel KJ, Moore EE, Albrecht RA, et al. Western trauma association critical decisions in trauma: management of rib fractures. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2017 Jan;82(1):200-3.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27779590?tool=bestpractice.com
Respiratory physical therapy
Rib fractures impair adequate ventilation resulting in atelectasis, poor oxygenation, and respiratory compromise.[27]Brasel KJ, Moore EE, Albrecht RA, et al. Western trauma association critical decisions in trauma: management of rib fractures. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2017 Jan;82(1):200-3.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27779590?tool=bestpractice.com
Early chest physical therapy and mobility are emphasized to improve pulmonary toilet (mucus and secretion clearance techniques). Breathing exercises assessed with incentive spirometry and assisted coughing may help prevent complications.[42]Battle C, Pelo C, Hsu J, et al. Expert consensus guidance on respiratory physiotherapy and rehabilitation of patients with rib fractures: an international, multidisciplinary e-Delphi study. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2023 Apr 1;94(4):578-83.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10045972
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36728349?tool=bestpractice.com
[56]Mukherjee K, Schubl SD, Tominaga G, et al. Non-surgical management and analgesia strategies for older adults with multiple rib fractures: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and joint practice management guideline from the Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma and the Chest Wall Injury Society. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2023 Mar 1;94(3):398-407.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36730672?tool=bestpractice.com
Treatment of underlying cause
Metastasis from lung, prostate, breast, and liver cancer can involve the ribs, accounting for 12.6% of metastatic lesions.[15]Xu DL, Zhang XT, Wang GH, et al. Clinical features of pathologically confirmed metastatic bone tumors: a report of 390 cases [in Chinese]. Ai Zheng. 2005 Nov;24(11):1404-7.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16552972?tool=bestpractice.com
Furthermore, there are numerous primary bone tumors that can present as pathologic rib fractures, including osteochondroma, enchondroma, plasmacytoma, chondrosarcoma, and osteosarcoma. About 37% of these lesions are malignant.[16]Aydoğdu K, Findik G, Agackiran Y, et al. Primary tumors of the ribs; experience with 78 patients. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2009 Aug;9(2):251-4.
https://academic.oup.com/icvts/article/9/2/251/729805
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19447801?tool=bestpractice.com
These should be managed with appropriate specialist referral and treatment.
As age increases, the absolute risk of sustaining a fragility fracture is inversely proportional to the patient's bone mineral density, with about 27% of these fractures occurring in the ribs.[4]Siris ES, Brenneman SK, Barrett-Connor E, et al. The effect of age and bone mineral density on the absolute, excess, and relative risk of fracture in postmenopausal women aged 50-99: results from the National Osteoporosis Risk Assessment (NORA). Osteoporos Int. 2006;17(4):565-74.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16392027?tool=bestpractice.com
Therefore, osteoporosis should be treated if present.
In children, the presence of rib fractures without associated trauma has the highest probability of being attributable to physical abuse when compared with all other fractures.[14]Kemp AM, Dunstan F, Harrison S, et al. Patterns of skeletal fractures in child abuse: systematic review. BMJ. 2008 Oct 2;337:a1518.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2563260/?tool=pubmed
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18832412?tool=bestpractice.com
Among infants younger than 12 months presenting with rib fractures, as many as 82% have sustained these injuries through physical abuse.[2]Bulloch B, Schubert CJ, Brophy PD, et al. Cause and clinical characteristics of rib fractures in infants. Pediatrics. 2000 Apr;105(4):E48.
http://pediatrics.aappublications.org/content/105/4/e48.full
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10742369?tool=bestpractice.com
[3]Paine CW, Fakeye O, Christian CW, et al. Prevalence of Abuse Among Young Children With Rib Fractures: A Systematic Review. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2019 Feb;35(2):96-103.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27749806?tool=bestpractice.com
A consultation with child protective services should be considered in all children with suspected physical abuse.
Management of complications
Pneumothorax occurs in about 14% to 37% of rib fractures, hemopneumothorax in 20% to 27%, pulmonary contusions in 17%, and a flail chest in up to 6%.[8]Sirmali M, Türüt H, Topçu S, et al. A comprehensive analysis of traumatic rib fractures: morbidity, mortality and management. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2003 Jul;24(1):133-8.
https://academic.oup.com/ejcts/article/24/1/133/375481
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12853057?tool=bestpractice.com
[9]Keel M, Meier C. Chest injuries - what is new? Curr Opin Crit Care. 2007 Dec;13(6):674-9.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17975389?tool=bestpractice.com
[10]Liman ST, Kuzucu A, Tastepe AI, et al. Chest injury due to blunt trauma. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2003 Mar;23(3):374-8.
http://ejcts.oxfordjournals.org/content/23/3/374.long
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12614809?tool=bestpractice.com
Traumatic injuries to the first rib have a 3% risk of concomitant great-vessel injury.[23]Gupta A, Jamshidi M, Rubin JR. Traumatic first rib fracture: is angiography necessary? A review of 730 cases. Cardiovasc Surg. 1997 Feb;5(1):48-53.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9158123?tool=bestpractice.com
A tube thoracostomy may be necessary to either decompress a pneumothorax or drain the hemothorax. See Pneumothorax.
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CT scan showing large left-sided pneumothoraxFrom the collection of Dr Paul Novakovich; used with permission [Citation ends].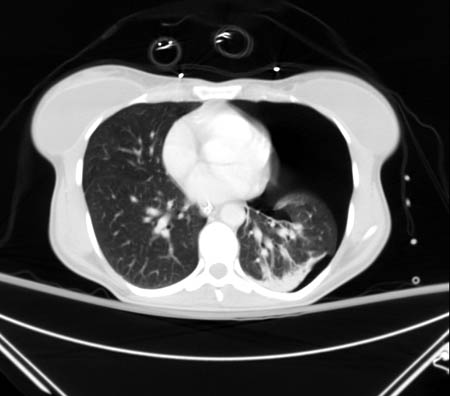 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CXR depicting the same pneumothorax as shown on CTFrom the collection of Dr Paul Novakovich; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CXR depicting the same pneumothorax as shown on CTFrom the collection of Dr Paul Novakovich; used with permission [Citation ends].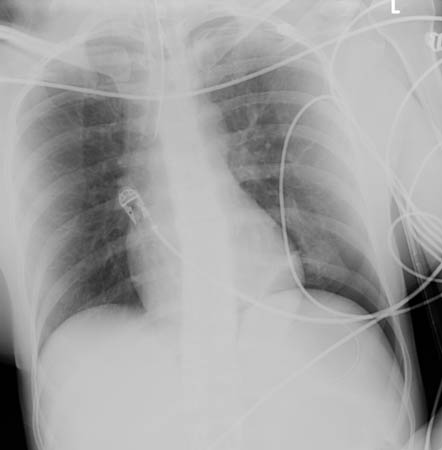
Because of the multitude of associated injuries, the treating physician should have a high suspicion for closed-head injuries, solid organ injuries, spine injuries, and extremity fractures. Consultation of the appropriate service should not be delayed if any associated injury is encountered.
Mechanical ventilation
Mechanical ventilation may be necessary for unstable patients.[56]Mukherjee K, Schubl SD, Tominaga G, et al. Non-surgical management and analgesia strategies for older adults with multiple rib fractures: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and joint practice management guideline from the Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma and the Chest Wall Injury Society. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2023 Mar 1;94(3):398-407.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36730672?tool=bestpractice.com
Isolated rib fractures rarely require mechanical ventilation unless associated with other injuries, such as pulmonary contusion.[60]Chest trauma. In: Hess DR, Kacmarek RM, eds. Essentials of mechanical ventilation. 3rd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Education; 2014. For patients with flail chest, mechanical ventilation is only needed if they present with shock, head injury, severe pulmonary dysfunction, or deteriorating respiratory status, or if immediate surgery is required.[60]Chest trauma. In: Hess DR, Kacmarek RM, eds. Essentials of mechanical ventilation. 3rd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Education; 2014. Internal fixation of ribs/flail chest may be considered in cases failing to wean from the ventilator, or when thoracotomy is required for other reasons.[61]Simon B, Ebert J, Bokhari F, et al; Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma. Management of pulmonary contusion and flail chest: an Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma practice management guideline. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012 Nov;73(5 Suppl 4):S351-61.
https://www.east.org/education/practice-management-guidelines
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23114493?tool=bestpractice.com
[62]Leinicke JA, Elmore L, Freeman BD, et al. Operative management of rib fractures in the setting of flail chest: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Surg. 2013 Dec;258(6):914-21.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23511840?tool=bestpractice.com
[63]Marasco SF, Davies AR, Cooper J, et al. Prospective randomized controlled trial of operative rib fixation in traumatic flail chest. J Am Coll Surg. 2013 May;216(5):924-32.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23415550?tool=bestpractice.com
There is a reported association between operative management of rib fractures in flail chest and reduced ventilator requirements, as well as earlier discharge from intensive care.[62]Leinicke JA, Elmore L, Freeman BD, et al. Operative management of rib fractures in the setting of flail chest: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Surg. 2013 Dec;258(6):914-21.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23511840?tool=bestpractice.com
[63]Marasco SF, Davies AR, Cooper J, et al. Prospective randomized controlled trial of operative rib fixation in traumatic flail chest. J Am Coll Surg. 2013 May;216(5):924-32.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23415550?tool=bestpractice.com
[64]Kasotakis G, Hasenboehler EA, Streib EW, et al. Operative fixation of rib fractures after blunt trauma: a practice management guideline from the Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2017 Mar;82(3):618-26.
https://journals.lww.com/jtrauma/Fulltext/2017/03000/Operative_fixation_of_rib_fractures_after_blunt.25.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28030502?tool=bestpractice.com
[65]Schuurmans J, Goslings JC, Schepers T. Operative management versus non-operative management of rib fractures in flail chest injuries: a systematic review. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2017 Apr;43(2):163-8.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5378742
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27572897?tool=bestpractice.com
This effect may be less pronounced in the presence of pulmonary contusion.[62]Leinicke JA, Elmore L, Freeman BD, et al. Operative management of rib fractures in the setting of flail chest: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Surg. 2013 Dec;258(6):914-21.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23511840?tool=bestpractice.com
Surgical stabilization
Surgical stabilization of rib fractures is not required in most patients with simple rib fractures. However, it may be considered in patients with multiple severely displaced rib fractures, or patients who fail to respond to optimal nonoperative management.[66]Pieracci FM, Majercik S, Ali-Osman F, et al. Consensus statement: surgical stabilization of rib fractures rib fracture colloquium clinical practice guidelines. Injury. 2017 Feb;48(2):307-21.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27912931?tool=bestpractice.com
[67]Lucena-Amaro S, Cole E, Zolfaghari P. Long term outcomes following rib fracture fixation in patients with major chest trauma. Injury. 2022 Sep;53(9):2947-52.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35513938?tool=bestpractice.com
In patients with flail chest, surgical stabilization should be considered on a case-by-case basis.[66]Pieracci FM, Majercik S, Ali-Osman F, et al. Consensus statement: surgical stabilization of rib fractures rib fracture colloquium clinical practice guidelines. Injury. 2017 Feb;48(2):307-21.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27912931?tool=bestpractice.com
[68]National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Insertion of metal rib reinforcements to stabilise a flail chest wall. Oct 2010. [internet publication].
http://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/IPG361
It is associated with reductions in:[64]Kasotakis G, Hasenboehler EA, Streib EW, et al. Operative fixation of rib fractures after blunt trauma: a practice management guideline from the Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2017 Mar;82(3):618-26.
https://journals.lww.com/jtrauma/Fulltext/2017/03000/Operative_fixation_of_rib_fractures_after_blunt.25.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28030502?tool=bestpractice.com
[67]Lucena-Amaro S, Cole E, Zolfaghari P. Long term outcomes following rib fracture fixation in patients with major chest trauma. Injury. 2022 Sep;53(9):2947-52.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35513938?tool=bestpractice.com
[68]National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Insertion of metal rib reinforcements to stabilise a flail chest wall. Oct 2010. [internet publication].
http://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/IPG361
[69]Wang Z, Jia Y, Li M. The effectiveness of early surgical stabilization for multiple rib fractures: a multicenter randomized controlled trial. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2023 Apr 10;18(1):118.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10084648
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/37038166?tool=bestpractice.com
Number of days spent on mechanical ventilation
Length of hospital stay
Length of intensive care stay
Rate of pneumonia
Need for tracheostomy
Degree of chest wall deformity
Cost of treatment.
However, any effect on mortality remains uncertain.[64]Kasotakis G, Hasenboehler EA, Streib EW, et al. Operative fixation of rib fractures after blunt trauma: a practice management guideline from the Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2017 Mar;82(3):618-26.
https://journals.lww.com/jtrauma/Fulltext/2017/03000/Operative_fixation_of_rib_fractures_after_blunt.25.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28030502?tool=bestpractice.com
In addition, the quality of the evidence upon which these recommendations are based is relatively poor.[66]Pieracci FM, Majercik S, Ali-Osman F, et al. Consensus statement: surgical stabilization of rib fractures rib fracture colloquium clinical practice guidelines. Injury. 2017 Feb;48(2):307-21.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27912931?tool=bestpractice.com
While surgical stabilization of fractures is now included within standard treatment, it is not widely practiced and requires ongoing trials in expert centers.
 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CXR depicting the same pneumothorax as shown on CTFrom the collection of Dr Paul Novakovich; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CXR depicting the same pneumothorax as shown on CTFrom the collection of Dr Paul Novakovich; used with permission [Citation ends].
