The Immunology of Neuromyelitis Optica—Current Knowledge, Clinical Implications, Controversies and Future Perspectives
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. The Definition of Neuromyelitis Optica
1.2. The History of NMO
1.3. Diagnostic Criteria for NMO and NMO Spectrum Disorders (NMOsd)
1.4. Clinical Features and Laboratory Findings
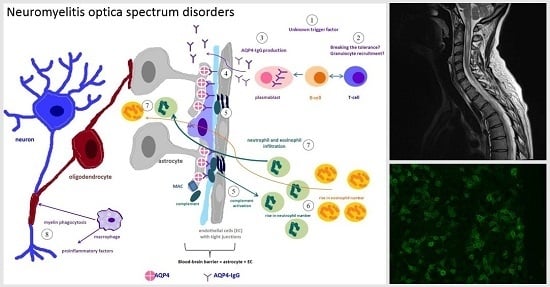
2. Immunopathogenesis of NMO
2.1. Immunopathological Findings in NMO
2.2. The Role of Several Cell Types in NMO Immunopathology
3. Autoantibodies against Aquaporin-4 (AQP4-IgG, NMO-IgG)
3.1. AQP4-IgG as a Specific NMO Biomarker
3.2. AQP4—Function, Structure, Expression in the CNS and Other Organs
3.3. The Role of AQP4-IgG in NMO Pathogenesis
3.3.1. Evidence Supporting Pathogenicity of AQP4-IgG in NMO
3.3.2. Synthesis of AQP4-IgG—Is It Only Peripheral or Also Intrathecal?
3.3.3. How Does AQP4-IgG Enter the Central Nervous System (CNS)?
3.3.4. How AQP4-IgG Immune Response Leads to Demyelination?
3.4. Detection of AQP4-IgG—Comparison of Sensitivity and Specificity of Different Assays
3.5. Serum Levels of AQP4-IgG—How Do They Change with Disease Activity and during Treatment?
3.6. Epidemiological and Clinical Differences between AQP4-IgG Seronegative and AQP4-IgG Seropositive NMO
3.7. AQP4-IgG Predictive Role
3.8. What Causes AQP4-IgG Seronegative NMO?
4. Autoantibodies against Aquaporin-1 (AQP1-Ab)
4.1. AQP1-Ab in NMOsd Patients
4.2. AQP1 Expression in the CNS
4.3. AQP1-Ab Mediated Immune Response and Its Possible Pathogenic Role in NMO
4.4. AQP1-Ab Assays
4.5. AQP1-Ab Specificity
4.6. Clinical Similarities and Differences between AQP1-Ab Seropositive and AQP4-IgG Seropositive NMO Patients
4.7. Is the AQP1-Ab a New Potential Biomarker for NMO?
5. Antibodies against Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein (MOG-IgG)
5.1. MOG-IgG in NMOsd Patients
5.2. MOG-IgG Expression in the CNS
5.3. How Does MOG-IgG Cause Lesions in the CNS and Is It Potentially Pathogenic in Vivo?
5.4. MOG-IgG Specificity
5.5. Clinical Characteristics of MOG-IgG Seropositive NMOsd Patients
5.6. MOG-IgG Seropositive Patients Treatment
5.7. MOG-IgG—Perspectives
6. Other Potential Biomarkers in NMO
7. NMO and Other Autoimmune Diseases
7.1. NMOsd in the Context of Other Autoimmune Diseases
7.2. Autoantibodies in NMOsd Patients
7.3. NMO in the Context of Myasthenia Gravis and Neoplasms
8. Treatment Strategies
8.1. Acute NMO Treatment: Methylprednisolone and Plasma Exchange
8.2. Maintenance Treatment
8.3. New Directions in the Treatment of NMO
9. Discussion
10. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AChR | neuromuscular junction acetylocholine receptor |
| ADCC | antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity |
| ADEM | acute disseminated encephalomyelitis |
| ANA | antinuclear antibodies |
| APC | antigen presenting cell |
| AQP1-Ab | aquaporin-1 antibody |
| AQP4-IgG | aquaporin-4 immunoglobulin G |
| BAFF | B-cell activating factor |
| BBB | blood-brain barrier |
| BMECs | human brain microvascular endothelial cells |
| CBA | cell-based assay |
| CCR3 | CC-chemokine receptor-3 |
| CDC | complement-depended cytotoxicity |
| CH50 | total hemolytic complement activity |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| CSF | cerebrospinal fluid |
| DTI | diffusion tensor imaging |
| EAAT2 | excitatory amino acid transporter 2 |
| EDSS | the Expanded Disability Status Scale |
| ELISA | enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| FIPA | fluoroimmunoprecipitation assay |
| FGF-basic | fibroblast growth factor-basic |
| G-CSF | granulocyte colony-stymulating factor |
| GFAP | glial fibrillary acid protein |
| GM-CSF | granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor |
| HEK | human embryonic kidney |
| HIMP | high-dose intravenous methylprednisolone therapy |
| HLAs | human leukocyte antigens |
| ICAM-1 | intercellular adhesion molecule-1 |
| IIF | indirect immunofluorescence assay |
| IL | interleukin |
| IL-1Ra | interleukin-1 receptor antagonist |
| IPND | International Panel for NMO Diagnosis |
| LETM | longitudinally extensive transverse meylitis |
| MAC | membrane attack complex |
| MBP | major basic protein |
| MG | myasthenia gravis |
| MIP-1β | macrophage inflammatory protein-1-β |
| MMP-9 | matrix metalloproteinase-9 |
| MOG-IgG | myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein immunoglobulin G |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| Gd (+) | gadolinium enhancing |
| MS | multiple sclerosis |
| MTR | magnetisation transfer |
| NE | neutrophil elastase |
| NMO | neuromyelitis optica |
| NMO-IgG | neuromyelitis optica immunoglobulin G |
| NMOsd | neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder |
| OAPs | orthogonal arrays of particles |
| ON | optic neuritis |
| PB | plasmablasts |
| PRES | posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome |
| RIPA | radioimmunoprecipitation assay |
| SEPs | posterior tibial nerve somatosensory-evoked potentials |
| sICAM-1 | soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1SLE: systemic lupus erythematosus |
| SS | Sjögren’s syndrome |
| sVCAM-1 | soluble vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 |
| TCZ | tocilizumab |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
| VCAM-1 | vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 |
| VEGF-A | vascular endothelial growth factor-A |
References
- Wingerchuk, D.M.; Hogancamp, W.F.; O’Brien, P.C.; Weinshenker, B.G. The clinical course of neuromyelitis optica (Devic’s syndrome). Neurology 1999, 53, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wingerchuk, D.M.; Lennon, V.A.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Pittock, S.J.; Weinshenker, B.G. The spectrum of neuromyelitis optica. Lancet Neurol. 2007, 6, 805–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingerchuk, D.M.; Lennon, V.A.; Pittock, S.J.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Weinshenker, B.G. Revised diagnostic criteria for neuromyelitis optica. Neurology 2006, 66, 1485–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarius, S.; Wildemann, B. The history of neuromyelitis optica. J. Neuroinflamm. 2013, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lennon, V.A.; Wingerchuk, D.M.; Kryzer, T.J.; Pittock, S.J.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Fujihara, K.; Nakashima, I.; Weinshenker, B.G. A serum autoantibody marker of neuromyelitis optica: Distinction from multiple sclerosis. Lancet 2004, 364, 2106–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennon, V.A.; Kryzer, T.J.; Pittock, S.J.; Verkman, A.S.; Hinson, S.R. IgG marker of optic-spinal multiple sclerosis binds to the aquaporin-4 water channel. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 202, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wingerchuk, D.M. Neuromyelitis spectrum disorders. Contin. Lifelong Learn. Neurol. 2010, 16, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wingerchuk, D.M.; Banwell, B.; Bennett, J.L.; Cabre, P.; Carroll, W.; Chitnis, T.; De Seze, J.; Fujihara, K.; Greenberg, B.; Jacob, A.; et al. International consensus diagnostic criteria for neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. Neurology 2015, 85, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulos, M.C.; Verkman, A.S. Aquaporin 4 and neuromyelitis optica. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matiello, M.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, W.; Brum, D.G.; Barreira, A.A.; Kingsbury, D.J.; Plant, G.T.; Adoni, T.; Weinshenker, B.G. Familial neuromyelitis optica. Neurology 2010, 75, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzartos, J.S.; Stergiou, C.; Kilidireas, K.; Zisimopoulou, P.; Thomaidis, T.; Tzartos, S.J. Anti-aquaporin-1 autoantibodies in patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadoun, S.; Waters, P.; Owens, G.P.; Bennett, J.L.; Vincent, A.; Papadopoulos, M.C. Neuromyelitis optica MOG-IgG causes reversible lesions in mouse brain. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2014, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucchinetti, C.F.; Mandler, R.N.; McGavern, D.; Bruck, W.; Gleich, G.; Ransohoff, R.M.; Trebst, C.; Weinshenker, B.; Wingerchuk, D.; Parisi, J.E.; et al. A role for humoral mechanisms in the pathogenesis of Devic’s neuromyelitis optica. Brain 2002, 125, 1450–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadoun, S.; Waters, P.; MacDonald, C.; Bell, B.A.; Vincent, A.; Verkman, A.S.; Papadopoulos, M.C. Neutrophil protease inhibition reduces neuromyelitis optica-immunoglobulin G-induced damage in mouse brain. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 71, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendriks, J.J.; Teunissen, C.E.; de Vries, H.E.; Dijkstra, C.D. Macrophages and neurodegeneration. Brain Res. Rev. 2005, 48, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradl, M.; Misu, T.; Takahashi, T.; Watanabe, M.; Mader, S.; Reindl, M.; Adzemovic, M.; Bauer, J.; Berger, T.; Fujihara, K.; et al. Neuromyelitis optica: Pathogenicity of patient immunoglobulin in vivo. Ann. Neurol. 2009, 66, 630–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segal, B.M. Th17 cells in autoimmune demyelinating disease. Semin. Immunopathol. 2010, 32, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.H.; Dai, Y.Q.; Qiu, W.; Lu, Z.Q.; Peng, F.H.; Wang, Y.G.; Bao, J.; Li, Y.; Hu, X.Q. Interleukin-17-secreting T cells in neuromyelitis optica and multiple sclerosis during relapse. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2011, 18, 1313–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Long, Y.; Lu, Z.; Hu, X. Increased memory Th17 cells in patients with neuromyelitis optica and multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2011, 234, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratelade, J.; Zhang, H.; Saadoun, S.; Bennett, J.L.; Papadopoulos, M.C.; Verkman, A.S. Neuromyelitis optica IgG and natural killer cells produce NMO lesions in mice without myelin loss. Acta Neuropathol. 2012, 123, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chihara, N.; Aranami, T.; Sato, W.; Miyazaki, Y.; Miyake, S.; Okamoto, T.; Ogawa, M.; Toda, T.; Yamamura, T. Interleukin 6 signaling promotes anti-aquaporin 4 autoantibody production from plasmablasts in neuromyelitis optica. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 3701–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, J.L.; Lam, C.; Kalluri, S.R.; Saikali, P.; Bautista, K.; Dupree, C.; Glogowska, M.; Case, D.; Antel, J.P.; Owens, G.P.; et al. Intrathecal pathogenic anti-aquaporin-4 antibodies in early neuromyelitis optica. Ann. Neurol. 2009, 66, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagelhus, E.A.; Ottersen, O.P. Physiological roles of aquaporin-4 in brain. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 1543–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, J.D.; Yeh, R.; Sandstrom, A.; Chorny, I.; Harries, W.E.; Robbins, R.A.; Miercke, L.J.; Stroud, R.M. Crystal structure of human aquaporin 4 at 1.8 Å and its mechanism of conductance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 7437–7442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, P.; Vincent, A. Detection of anti-aquaporin-4 antibodies in neuromyelitis optica: Current status of the assays. Int. MS J. 2008, 15, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nicchia, G.P.; Mastrototaro, M.; Rossi, A.; Pisani, F.; Tortorella, C.; Ruggieri, M.; Lia, A.; Trojano, M.; Frigeri, A.; Svelto, M. Aquaporin-4 orthogonal arrays of particles are the target for neuromyelitis optica autoantibodies. Glia 2009, 57, 1363–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crane, J.M.; Lam, C.; Rossi, A.; Gupta, T.; Bennett, J.L.; Verkman, A.S. Binding affinity and specificity of neuromyelitis optica autoantibodies to aquaporin-4 M1/M23 isoforms and orthogonal arrays. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 16516–16524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phuan, P.-W.; Ratelade, J.; Rossi, A.; Tradtrantip, L.; Verkman, A.S. Complement-dependent cytotoxicity in neuromyelitis optica requires aquaporin-4 protein assembly in orthogonal arrays. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 13829–13839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, T.; Fujihara, K.; Nakashima, I.; Misu, T.; Miyazawa, I.; Nakamura, M.; Watanabe, S.; Shiga, Y.; Kanaoka, C.; Fujimori, J.; et al. Anti-aquaporin-4 antibody is involved in the pathogenesis of NMO: A study on antibody titre. Brain 2007, 130, 1235–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarius, S.; Aboul-Enein, F.; Waters, P.; Kuenz, B.; Hauser, A.; Berger, T.; Lang, W.; Reindl, M.; Vincent, A.; Kristoferitsch, W. Antibody to aquaporin-4 in the long-term course of neuromyelitis optica. Brain 2008, 131, 3072–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinson, S.R.; McKeon, A.; Lennon, V.A. Neurological autoimmunity targeting aquaporin-4. Neuroscience 2010, 168, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinson, S.R.; Roemer, S.F.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Fryer, J.P.; Kryzer, T.J.; Chamberlain, J.L.; Howe, C.L.; Pittock, S.J.; Lennon, V.A. Aquaporin-4-binding autoantibodies in patients with neuromyelitis optica impair glutamate transport by down-regulating EAAT2. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 2473–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, T.; Saikali, P.; Cayrol, R.; Roth, A.D.; Bar-Or, A.; Prat, A.; Antel, J.P. Functional consequences of neuromyelitis optica-IgG astrocyte interactions on blood-brain barrier permeability and granulocyte recruitment. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 5730–5737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takano, R.; Misu, T.; Takahashi, T.; Izumiyama, M.; Fujihara, K.; Itoyama, Y. A prominent elevation of glial fibrillary acidic protein in the cerebrospinal fluid during relapse in neuromyelitis optica. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2008, 215, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misu, T.; Takano, R.; Fujihara, K.; Takahashi, T.; Sato, S.; Itoyama, Y. Marked increase in cerebrospinal fluid glial fibrillar acidic protein in neuromyelitis optica: An astrocytic damage marker. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2009, 80, 575–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadoun, S.; Waters, P.; Bell, B.A.; Vincent, A.; Verkman, A.S.; Papadopoulos, M.C. Intra-cerebral injection of neuromyelitis optica immunoglobulin G and human complement produces neuromyelitis optica lesions in mice. Brain 2010, 133, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nytrova, P.; Potlukova, E.; Kemlink, D.; Woodhall, M.; Horakova, D.; Waters, P.; Havrdova, E.; Zivorova, D.; Vincent, A.; Trendelenburg, M. Complement activation in patients with neuromyelitis optica. J. Neuroimmunol. 2014, 274, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tüzün, E.; Kürtüncü, M.; Türkoğlu, R.; İçöz, S.; Pehlivan, M.; Birişik, Ö.; Eraksoy, M.; Akman-Demir, G. Enhanced complement consumption in neuromyelitis optica and Behcet’s disease patients. J. Neuroimmunol. 2011, 233, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroda, H.; Fujihara, K.; Takano, R.; Takai, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Misu, T.; Nakashima, I.; Sato, S.; Itoyama, Y.; Aoki, M. Increase of complement fragment C5a in cerebrospinal fluid during exacerbation of neuromyelitis optica. J. Neuroimmunol. 2013, 254, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinoshita, M.; Nakatsuji, Y.; Kimura, T.; Moriya, M.; Takata, K.; Okuno, T.; Kumanogoh, A.; Kajiyama, K.; Yoshikawa, H.; Sakoda, S. Neuromyelitis optica: Passive transfer to rats by human immunoglobulin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 386, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarius, S.; Ruprecht, K.; Wildemann, B.; Kuempfel, T.; Ringelstein, M.; Geis, C.; Kleiter, I.; Kleinschnitz, C.; Berthele, A.; Brettschneider, J.; et al. Contrasting disease patterns in seropositive and seronegative neuromyelitis optica: A multicentre study of 175 patients. J. Neuroinflammation 2012, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jarius, S.; Franciotta, D.; Paul, F.; Ruprecht, K.; Bergamaschi, R.; Rommer, P.S.; Reuss, R.; Probst, C.; Kristoferitsch, W.; Wandinger, K.P.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid antibodies to aquaporin-4 in neuromyelitis optica and related disorders: Frequency, origin, and diagnostic relevance. J. Neuroinflamm. 2010, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, M.; Takahashi, T.; Kawai, M.; Fujihara, K.; Kanda, T. A serological analysis of viral and bacterial infections associated with neuromyelitis optica. J. Neurol. Sci. 2011, 300, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, E.T.; Inman, C.B.; Weller, R.O. Interrelationships of the pia mater and the perivascular (Virchow–Robin) spaces in the human cerebrum. J. Anat. 1990, 170, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Broadwell, R.D.; Sofroniew, M.V. Serum proteins bypass the blood-brain fluid barriers for extracellular entry to the central nervous system. Exp. Neurol. 1993, 120, 245–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlingemann, R.O. Lack of blood–brain barrier properties in microvessels of the prelaminar optic nerve head. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2001, 42, 895–901. [Google Scholar]
- Bartanusz, V.; Jezova, D.; Alajajian, B.; Digicaylioglu, M. The blood–spinal cord barrier: Morphology and clinical implications. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 70, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misu, T.; Fujihara, K.; Kakita, A.; Konno, H.; Nakamura, M.; Watanabe, S.; Takahashi, T.; Nakashima, I.; Takahashi, H.; Itoyama, Y. Loss of aquaporin 4 in lesions of neuromyelitis optica: Distinction from multiple sclerosis. Brain 2007, 130, 1224–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, P.; Jarius, S.; Littleton, E.; Leite, M.I.; Jacob, S.; Gray, B.; Geraldes, R.; Vale, T.; Jacob, A.; Palace, J.; et al. Aquaporin-4 antibodies in neuromyelitis optica and longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis. Arch. Neurol. 2008, 65, 913–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, F.; Jarius, S.; Aktas, O.; Bluthner, M.; Bauer, O.; Appelhans, H.; Franciotta, D.; Bergamaschi, R.; Littleton, E.; Palace, J.; et al. Antibody to aquaporin 4 in the diagnosis of neuromyelitis optica. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayakawa, S.; Mori, M.; Okuta, A.; Kamegawa, A.; Fujiyoshi, Y.; Yoshiyama, Y.; Mitsuoka, K.; Ishibashi, K.; Sasaki, S.; Hattori, T.; et al. Neuromyelitis optica and anti-aquaporin-4 antibodies measured by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J. Neuroimmunol. 2008, 196, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, P.J.; McKeon, A.; Leite, M.I.; Rajasekharan, S.; Lennon, V.A.; Villalobos, A.; Palace, J.; Mandrekar, J.N.; Vincent, A.; Bar-Or, A.; et al. Serologic diagnosis of NMO A multicenter comparison of aquaporin-4-IgG assays. Neurology 2012, 78, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rash, J.E.; Davidson, K.G.V.; Yasumura, T.; Furman, C.S. Freeze-fracture and immunogold analysis of aquaporin-4 (AQP4) square arrays, with models of AQP4 lattice assembly. Neuroscience 2004, 129, 915–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinson, S.R.; McKeon, A.; Fryer, J.P.; Apiwattanakul, M.; Lennon, V.A.; Pittock, S.J. Prediction of neuromyelitis optica attack severity by quantitation of complement-mediated injury to aquaporin-4-expressing cells. Arch. Neurol. 2009, 66, 1164–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, A.; Matsushita, T.; Doi, H.; Matsuoka, T.; Shigeto, H.; Isobe, N.; Kawano, Y.; Tobimatsu, S.; Kira, J. Multimodality-evoked potential study of anti-aquaporin-4 antibody-positive and-negative multiple sclerosis patients. J. Neurol. Sci. 2009, 281, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinshenker, B.G.; Wingerchuk, D.M.; Vukusic, S.; Linbo, L.; Pittock, S.J.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Lennon, V.A. Neuromyelitis optica IgG predicts relapse after longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis. Ann. Neurol. 2006, 59, 566–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melamed, E.; Levy, M.; Waters, P.J.; Sato, D.K.; Bennett, J.L.; John, G.R.; Hooper, D.C.; Saiz, A.; Bar-Or, A.; Kim, H.J.; et al. Update on biomarkers in neuromyelitis optica. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 2, e134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Shan, F.; Chen, M.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, B.; Gao, C.; Gao, Q.; Yang, N. Development of a cell-based assay for the detection of anti-aquaporin 1 antibodies in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. J. Neuroimmunol. 2014, 273, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tüzün, E.; Tzartos, J.; Ekizoğlu, E.; Stergiou, C.; Zisimopoulou, P.; Çoban, A.; Shugaiv, E.; Türkoğlu, R.; Kürtüncü, M.; Baykan, B.; et al. Aquaporin-1 Antibody in Neuromyelitis Optica Patients. Eur. Neurol. 2014, 72, 271–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mader, S.; Gredler, V.; Schanda, K.; Rostasy, K.; Dujmovic, I.; Pfaller, K.; Lutterotti, A.; Jarius, S.; Di Pauli, F.; Kuenz, B.; et al. Complement activating antibodies to myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein in neuromyelitis optica and related disorders. J. Neuroinflamm. 2011, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, D.K.; Callegaro, D.; Lana-Peixoto, M.A.; Waters, P.J.; de Haidar Jorge, F.M.; Takahashi, T.; Nakashima, I.; Apostolos-Pereira, S.L.; Talim, N.; Simm, R.F.; et al. Distinction between MOG antibody-positive and AQP4 antibody-positive NMO spectrum disorders. Neurology 2014, 82, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanathan, S.; Reddel, S.W.; Henderson, A.; Parratt, J.D.; Barnett, M.; Gatt, P.N.; Merheb, V.; Kumaran, R.-Y.A.; Pathmanandavel, K.; Sinmaz, N.; et al. Antibodies to myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein in bilateral and recurrent optic neuritis. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2014, 1, e40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wingerchuk, D.M.; Weinshenker, B.G. The emerging relationship between neuromyelitis optica and systemic rheumatologic autoimmune disease. Mult. Scler. J. 2012, 18, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzawa, A.; Mori, M.; Arai, K.; Sato, Y.; Hayakawa, S.; Masuda, S.; Taniguchi, J.; Kuwabara, S. Cytokine and chemokine profiles in neuromyelitis optica: Significance of interleukin-6. Mult. Scler. Houndmills Basingstoke Engl. 2010, 16, 1443–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzawa, A.; Mori, M.; Ito, M.; Uchida, T.; Hayakawa, S.; Masuda, S.; Kuwabara, S. Markedly increased CSF interleukin-6 levels in neuromyelitis optica, but not in multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. 2009, 256, 2082–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzawa, A.; Mori, M.; Sawai, S.; Masuda, S.; Muto, M.; Uchida, T.; Ito, S.; Nomura, F.; Kuwabara, S. Cerebrospinal fluid interleukin-6 and glial fibrillary acidic protein levels are increased during initial neuromyelitis optica attacks. Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 2013, 421, 181–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, K.; Zhong, X.; Dai, Y.; Qiu, W.; Wu, A.; Hu, X. Notable increased cerebrospinal fluid levels of soluble interleukin-6 receptors in neuromyelitis optica. Neuroimmunomodulation 2012, 19, 304–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzawa, A.; Mori, M.; Sato, Y.; Masuda, S.; Kuwabara, S. CSF interleukin-6 level predicts recovery from neuromyelitis optica relapse. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2012, 83, 339–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosokawa, T.; Nakajima, H.; Doi, Y.; Sugino, M.; Kimura, F.; Hanafusa, T.; Takahashi, T. Increased serum matrix metalloproteinase-9 in neuromyelitis optica: Implication of disruption of blood-brain barrier. J. Neuroimmunol. 2011, 236, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, F.; Sano, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Haruki, H.; Saito, K.; Koga, M.; Kanda, T. Sera from neuromyelitis optica patients disrupt the blood-brain barrier. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2012, 83, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzawa, A.; Mori, M.; Masuda, S.; Kuwabara, S. Markedly elevated soluble intercellular adhesion molecule 1, soluble vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 levels, and blood-brain barrier breakdown in neuromyelitis optica. Arch. Neurol. 2011, 68, 913–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKeon, A.; Lennon, V.A.; Jacob, A.; Matiello, M.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Kale, N.; Chan, K.H.; Weinshenker, B.G.; Apiwattinakul, M.; Wingerchuk, D.M.; et al. Coexistence of myasthenia gravis and serological markers of neurological autoimmunity in neuromyelitis optica. Muscle Nerve 2009, 39, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittock, S.J.; Lennon, V.A. Aquaporin-4 autoantibodies in a paraneoplastic context. Arch. Neurol. 2008, 65, 629–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collongues, N.; de Seze, J. Current and future treatment approaches for neuromyelitis optica. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2011, 4, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, A.; Matiello, M.; Weinshenker, B.G.; Wingerchuk, D.M.; Lucchinetti, C.; Shuster, E.; Carter, J.; Keegan, B.M.; Kantarci, O.H.; Pittock, S.J. Treatment of neuromyelitis optica with mycophenolate mofetil: Retrospective analysis of 24 patients. Arch. Neurol. 2009, 66, 1128–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinstock-Guttman, B.; Ramanathan, M.; Lincoff, N.; Napoli, S.Q.; Sharma, J.; Feichter, J.; Bakshi, R. Study of mitoxantrone for the treatment of recurrent neuromyelitis optica (Devic disease). Arch. Neurol. 2006, 63, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakker, J.; Metz, L. Devic’s neuromyelitis optica treated with intravenous gamma globulin (IVIG). Can. J. Neurol. Sci. J. Can. Sci. Neurol. 2004, 31, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, A.; Weinshenker, B.G.; Violich, I.; McLinskey, N.; Krupp, L.; Fox, R.J.; Wingerchuk, D.M.; Boggild, M.; Constantinescu, C.S.; Miller, A.; et al. Treatment of neuromyelitis optica with rituximab: Retrospective analysis of 25 patients. Arch. Neurol. 2008, 65, 1443–1448. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tradtrantip, L.; Zhang, H.; Saadoun, S.; Phuan, P.-W.; Lam, C.; Papadopoulos, M.C.; Bennett, J.L.; Verkman, A.S. Anti-Aquaporin-4 monoclonal antibody blocker therapy for neuromyelitis optica. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 71, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittock, S.J.; Lennon, V.A.; McKeon, A.; Mandrekar, J.; Weinshenker, B.G.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; O’Toole, O.; Wingerchuk, D.M. Eculizumab in AQP4-IgG-positive relapsing neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders: An open-label pilot study. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, M.; Matsuoka, T.; Miyamoto, K.; Kusunoki, S.; Okamoto, T.; Murata, M.; Miyake, S.; Aranami, T.; Yamamura, T. Efficacy of the anti-IL-6 receptor antibody tocilizumab in neuromyelitis optica A pilot study. Neurology 2014, 82, 1302–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jasiak-Zatonska, M.; Kalinowska-Lyszczarz, A.; Michalak, S.; Kozubski, W. The Immunology of Neuromyelitis Optica—Current Knowledge, Clinical Implications, Controversies and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 273. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17030273
Jasiak-Zatonska M, Kalinowska-Lyszczarz A, Michalak S, Kozubski W. The Immunology of Neuromyelitis Optica—Current Knowledge, Clinical Implications, Controversies and Future Perspectives. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(3):273. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17030273
Chicago/Turabian StyleJasiak-Zatonska, Michalina, Alicja Kalinowska-Lyszczarz, Slawomir Michalak, and Wojciech Kozubski. 2016. "The Immunology of Neuromyelitis Optica—Current Knowledge, Clinical Implications, Controversies and Future Perspectives" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 3: 273. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17030273
APA StyleJasiak-Zatonska, M., Kalinowska-Lyszczarz, A., Michalak, S., & Kozubski, W. (2016). The Immunology of Neuromyelitis Optica—Current Knowledge, Clinical Implications, Controversies and Future Perspectives. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(3), 273. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17030273